Astronomers have used the Occasion Horizon Telescope (EHT) to watch a violent cosmic dance between a suspected pair of supermassive black holes on the coronary heart of a distant galaxy. The proof for this tryst between cosmic monsters lies within the twisted properties of the jets that erupt across the black holes.
The supermassive black gap pair, or binary, lurks on the coronary heart of the quasar OJ287, positioned on the middle of a galaxy round 1.6 billion light-years away from Earth. Utilizing a degree of decision that might be capable of spot a tennis ball on the floor of the moon, the crew noticed two shockwaves flowing down the jet of OJ287. The shocks, apparently, have been seen touring at completely different speeds. And as they journey, passing via robust magnetic fields, these shockwaves seem to supply a phenomenon by no means seen earlier than.
Since then, the EHT has continued to make waves in black gap science.
“This end result exhibits that the EHT will not be solely helpful for producing spectacular photographs, however can be used to grasp the physics that govern black gap jets,” EHT crew member Mariafelicia De Laurentis mentioned in a press release. “Distinguishing observationally between what is because of geometry and what’s as an alternative the results of actual bodily processes is a key step in evaluating theoretical fashions with observations.”
Snapshots of a black gap jet
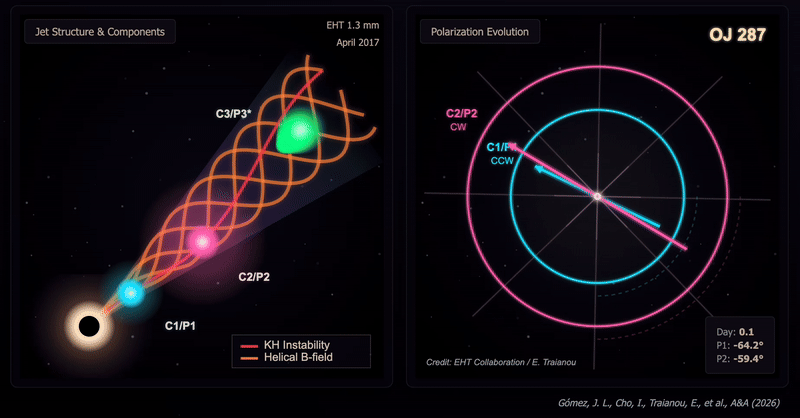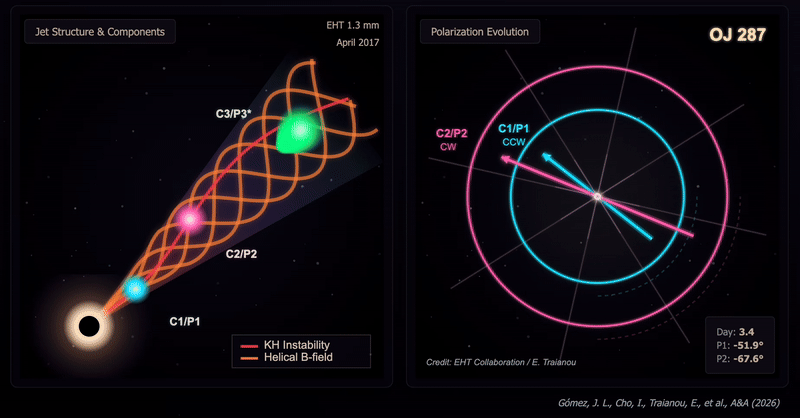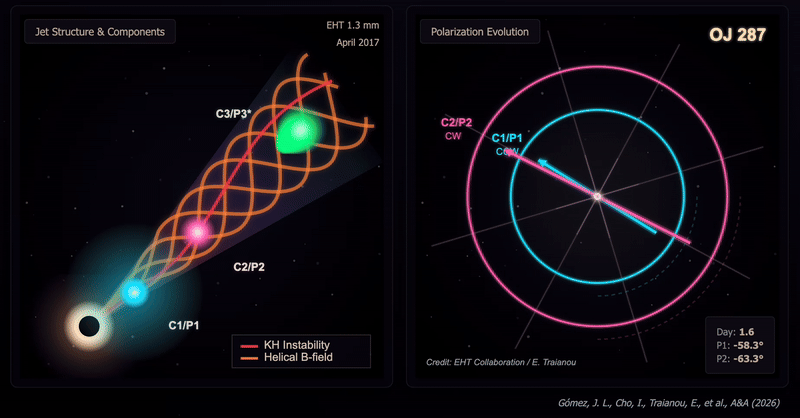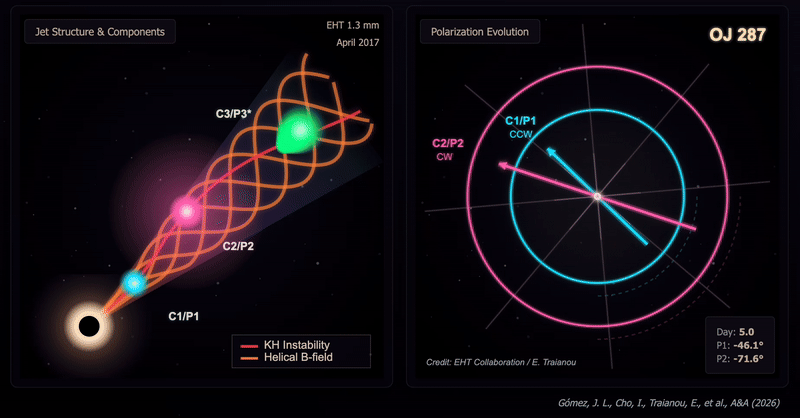
The crew captured two snapshots of the OJ287 system on April 5, 2017, after which on April 10 in the identical yr. These revealed substantial modifications in each the construction and polarization of the OJ287 that occurred over the course of simply 5 Earth days. That’s the shortest interval over which such modifications have been noticed in a black gap jet.
These modifications are regarded as the results of shocks interacting with instabilities in velocity known as Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities. They lead to a extremely twisted construction inside a jet, with three distinct polarized parts: two slower and rotating in reverse instructions to at least one one other, one quicker and rotating counterclockwise. This represented the primary direct affirmation of a helical magnetic subject with the jet of a black gap.
“We’re spatially resolving the person shock parts and observing their interplay with Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities,” crew member Ilje Cho of the Korea Institute for Astronomy and House Science mentioned. “That is the primary time we’ve got instantly noticed this interplay between shocks and instabilities in a black gap jet.”
“These noticed variations within the jet are normally interpreted when it comes to a precession impact of the jet itself. Nevertheless, precession fashions would anticipate the jet parts to maneuver ballistically alongside the jet,” EHT crew member Rocco Lico of the Italian Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) mentioned. “Our observations, nonetheless, point out non-ballistic motions of those parts, calling into query the precession speculation as the only real rationalization for the noticed morphology of the supply.” The speedy motions measured by the crew urged the kinetic vitality of the particles exceeds the magnetic vitality inside the inner areas of the jet. This favors the event of Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities, which come up as a result of distinction in velocity on the floor between the jet, which strikes at speeds approaching light-speed, and the a lot slower surrounding matter. These instabilities could cause helix-shaped distortions that manifest as a “twisted” construction, identical to that which the EHT noticed within the OJ287 jet.
The twisted construction of the jet noticed in OJ287, the excessive diploma of polarization of the three parts, and the evolution of their polarization angles, point out a fancy interplay between Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities and shocks in a jet permeated by a helical magnetic subject.
“These rotations in reverse instructions are the smoking gun,” analysis crew chief José L. Gómez of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía-Csic mentioned within the assertion. “When the shock wave parts work together with the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability, they illuminate completely different phases of the helical construction of the magnetic subject, producing the polarization oscillations we observe.”
The crew’s mannequin proposes that the Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities generate filamentary constructions that work together with propagating shocks within the jet.
“These interactions compress the magnetic subject and amplify the emission in particular areas of the jet, explaining the noticed options in each complete depth and polarized mild, in addition to the speedy variations in polarization angles and the obvious non-ballistic motions noticed, regardless of the presence of a globally rectilinear jet,” Lico mentioned. “For the primary time, high-resolution EHT knowledge permit us to instantly visualize these constructions, offering concrete proof of the interplay between jet instabilities, shocks, and helical magnetic fields.”
OJ287 was the best candidate to make these observations as a result of the dancing supermassive black holes on this pair are well-known for his or her periodic outbursts, making it a novel laboratory to check black gap physics.
The crew’s analysis was printed on Jan. 8 within the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.