Sept. 14, 2015, was one of the crucial essential days in science historical past. It marked the first-ever detection of gravitational waves, tiny ripples in space-time (the four-dimensional union of house and time), a milestone notched by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO).
Since that day, LIGO — composed of two extremely delicate laser interferometers situated in Hanford, Washington and Livingston, Louisiana — has been joined by two smaller gravitational wave observatories: Virgo, which got here on-line in Italy on Aug. 1, 2017, and the Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA) situated in Japan, in late 2019.
Over the course of 4 working runs, separated by shutdowns to permit for enhancements and upgrades, the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA devices have develop into so delicate that they’ll now measure distortions in space-time attributable to gravitational waves which are 1/10,000 the width of a proton, or 700 trillion occasions smaller than the width of a human hair. Collectively, the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA collaboration has now detected over 300 gravitational wave alerts, opening a totally new window to the universe that permits scientists to listen to a few of the most excessive and violent cosmic occasions.
Right here, Area.com takes you thru a few of the most essential gravitational wave breakthroughs which have occurred since 2015.
Whereas these milestones are available no specific order, there is just one place we are able to begin…
1. Proving Einstein proper! The primary gravitational wave detection
On Sept. 14, 2015, ripples in space-time washed over Earth that have been generated by the merger of two black holes, every with a mass of round 30 occasions that of the solar. This sign, which might come to be referred to as GW150914 (GW for “gravitational wave” and the next numbers for the date of measurement), had been touring to our planet for 1.4 billion years.
GW150914’s arrival and detection confirmed a idea that was first proposed a century earlier by arguably historical past’s most well-known physicist, Albert Einstein, in his 1915 idea of gravity, normal relativity.
Basic relativity predicts that objects with mass trigger the very material of space-time to warp, with gravity arising from this warp. The bigger the mass of an object, the higher the warp in space-time it generates, and thus the stronger its gravitational affect.
However normal relativity additionally instructed that, when objects speed up, they need to generate ripples in space-time — gravitational waves. These can be important sufficient to measure just for objects of really huge standing, resembling black holes swirling round one another in a binary system and finally merging.
Introduced to the general public on Feb. 11, 2016, GW150914 represented additional validation of normal relativity and confirmed that black gap mergers really happen, creating extra huge “daughter” black holes. The discover additionally gave scientists a separate option to examine the universe alongside “conventional” astronomy, which depends largely on the detection and examine of sunshine.
The achievement would earn Rainer Weiss, who handed away simply final month, Kip Thorne and Barry Barish the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics.
2. Heaviest black gap merger
On Nov. 23, 2023, LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA (LVK) detected the gravitational wave sign GW231123, which concerned a conflict between black holes with plenty 100 and 140 occasions that of the solar. This collision created a daughter black gap with a mass round 225 occasions that of the solar, with the lacking mass transformed toa gravitational wave “screech” (which you’ll be able to study extra about beneath).
This was essentially the most huge black gap merger detected in gravitational waves thus far, with the prior file holder being 2021’s GW190521, which was resulted in a daughter black gap with 140 photo voltaic plenty.
“That is essentially the most huge black gap binary we have noticed by gravitational waves, and it presents an actual problem to our understanding of black gap formation,” LVK collaboration member and Cardiff College researcher Mark Hannam mentioned of GW231123. “Black holes this huge are forbidden by commonplace stellar evolution fashions.
“One risk is that the 2 black holes on this binary fashioned by earlier mergers of smaller black holes.”
3. This neutron star merger was golden!
It is not all black gap mergers for LKV. The gravitational wave detectors have additionally “heard” ripples in space-time from clashes between neutron stars. These are excessive stellar remnants composed of the densest matter within the recognized universe that, like stellar-mass black holes, are born when huge stars go supernova and die.
On Aug. 17, 2017, LIGO and Virgo detected a sign, GW170817, representing gravitational waves from a collision between neutron stars situated round 130 million light-years from Earth. This was the primary detection of gravitational waves from something apart from black holes.
This was an essential scientific breakthrough, as a result of it’s thought that mergers between neutron stars generate the one surroundings that’s excessive and violent sufficient to permit the fusion processes that may generate parts heavier than iron, like gold, silver and plutonium.

“It instantly appeared to us the supply was more likely to be neutron stars, the opposite coveted supply we have been hoping to see — and promising the world we’d see,” David Shoemaker, spokesperson for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and senior analysis scientist on the Massachusetts Institute of Expertise’s (MIT) Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Area Analysis, mentioned in a press release on the time. “From informing detailed fashions of the internal workings of neutron stars and the emissions they produce to extra basic physics resembling normal relativity, this occasion is simply so wealthy. It’s a reward that can carry on giving.”
GW170817 was humanity’s first step towards understanding how the gold in your jewellery field was cast. However this listing is not finished with this occasion simply but; its significance to science goes past the primary detection of a neutron star merger.
4. Better of each worlds: Multimessenger astronomy is born!
As you may think, when stellar remnants as excessive as neutron stars collide, there’s fairly a burst of power, and never simply in gravitational waves, which could be thought-about gravitational radiation.
Neutron star mergers are additionally accompanied by flashes of sunshine that astronomers have dubbed “kilonovas.” Thus, the primary detection of a neutron star merger in gravitational waves supplied scientists the distinctive alternative to observe this up with “conventional astronomy,” which makes use of completely different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum.
This led to GW170817 turning into one of the crucial broadly studied astronomical occasions in historical past, with practically one-third of the world’s electromagnetic astronomers chasing the gravitational wave detection through conventional astronomy.
Such work paid off, with NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray spacecraft and Europe’s INTEGRAL (Worldwide Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory) each independently detecting a gamma-ray burst designated GRB 170817A erupting from this similar merger.
This allowed astronomers to find out that the neutron star merger occurred within the galaxy NGC 4993, situated about 140 million light-years away.
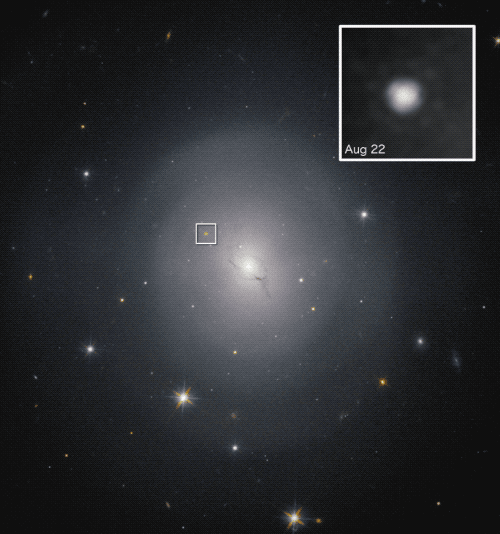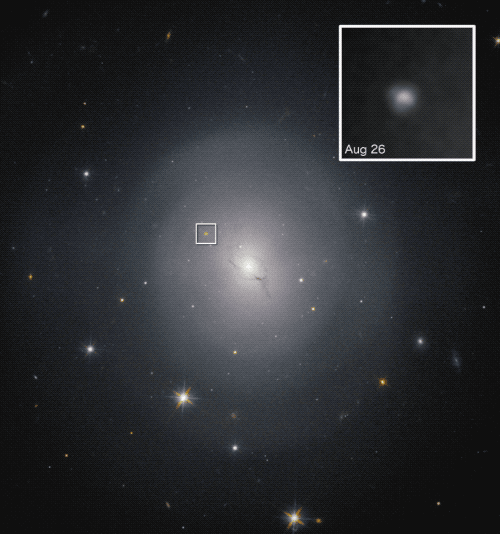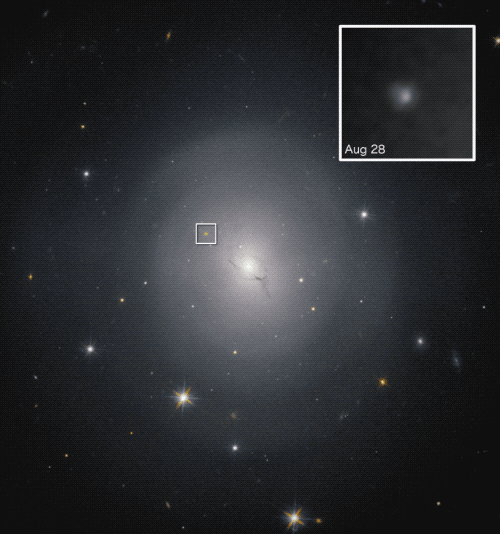
This was the primary profitable utility of “multimessenger astronomy,” which observes cosmic occasions utilizing multiple type of messenger — on this case, gravitational waves and electromagnetic radiation. The third spoke on this wheel is messengers within the type of high-energy particles, resembling neutrinos or cosmic rays generated by cosmic occasions.
The truth that every of those “messengers” is created by a special astrophysical course of means they’ve the potential to disclose completely different details about the identical supply. That makes multimessenger astronomy a strong new device in science.
Up to now, the occasion that generated GW170817 and launched GRB 170817A stays the one profitable remark of an occasion in each gravitational waves and electromagnetic radiation.
“It’s tremendously thrilling to expertise a uncommon occasion that transforms our understanding of the workings of the universe,” France Córdova, then the director of the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis (NSF), which funds LIGO, mentioned in a press release on the time. “This discovery realizes a long-standing objective many people have had — that’s, to concurrently observe uncommon cosmic occasions utilizing each conventional and gravitational-wave observatories.”
5. For whom the black gap tolls
The emission of gravitational waves from a binary black gap merger is available in three phases. As these orbiting black holes emit gravitational waves, their orbits tighten as a result of lack of angular momentum from the system. This results in the 2 black holes finally colliding and merging, sending out a high-pitched gravitational wave “screech” adopted by a diminishing “ringdown” of vibrations lasting for a fraction of a second.
“The [daughter] black gap is much like a bell that rings, producing a spectrum of a number of fading tones that encode details about the bell,” Collin Capano from the Albert Einstein Institute mentioned in a press release again in 2023, after he and his colleagues revealed that that they had discovered sturdy observational proof of at the least two gravitational-wave frequencies current in a binary black gap ringdown sign.
This ringdown sign, the aforementioned GW190521, can provide particulars of the mass and spin of a resultant daughter black gap, to nice precision.
“Reaching this multimode remark – in different phrases, the detection of two distinct vibration frequencies of a deformed black gap – has been a welcome shock. It was broadly assumed this may not be attainable earlier than the following era of gravitational-wave detectors,” Capino mentioned.
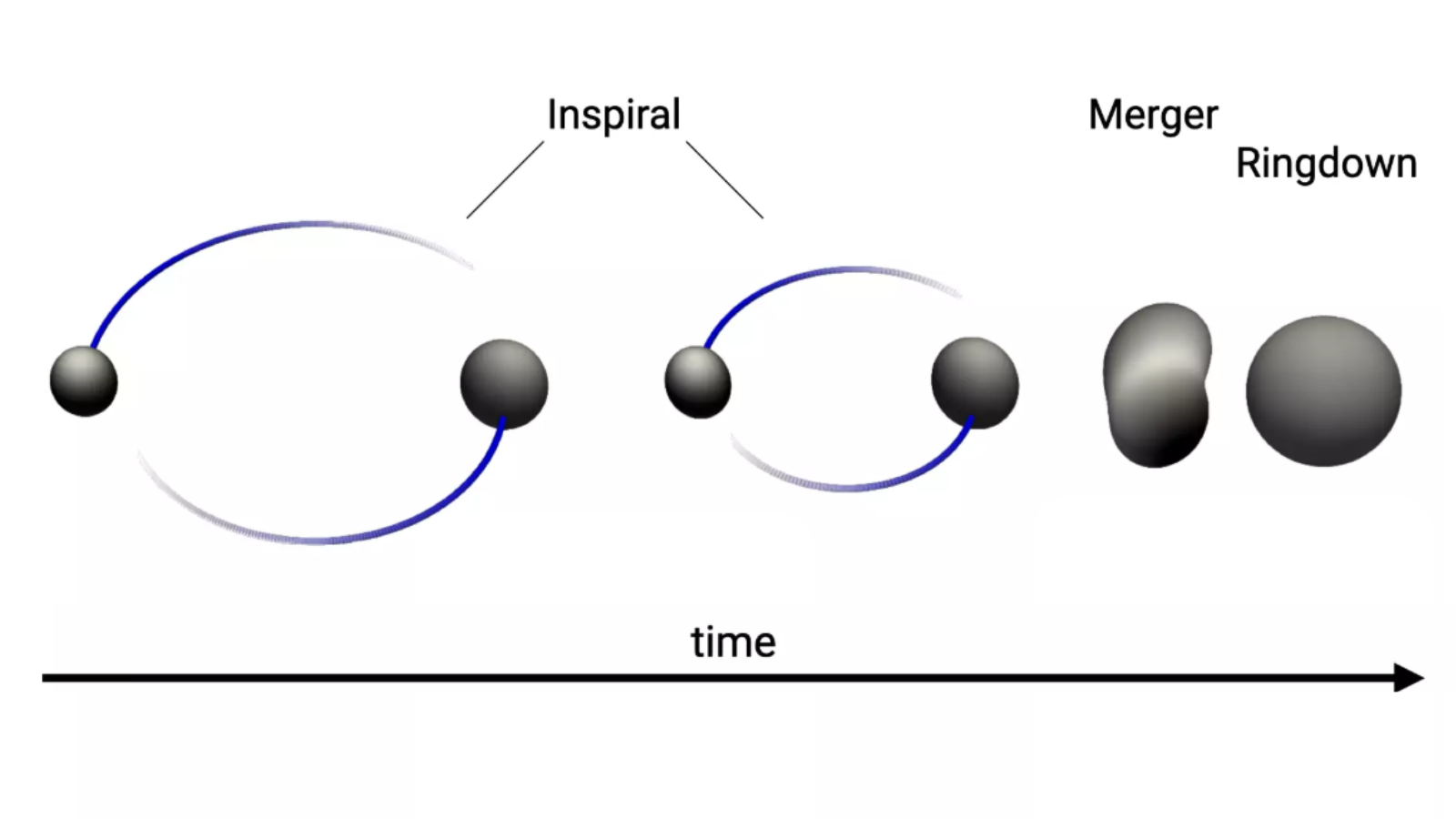
The GW190521 ringdown was additionally important as a result of it acted as a take a look at of the concept black holes could be described by simply three traits: their mass, spin and electrical cost. This idea is immortalized by physicist John Wheeler’s notorious phrase: “Black holes haven’t any hair.”
“GW190521 handed the take a look at and we discovered no indicators of any black gap physics past Einstein’s normal idea of relativity,” Capino’s colleague Julian Westerweck mentioned again in 2023. “It’s fairly outstanding {that a} idea that’s over 100 years previous now continues to work so properly.”
6. Combine it up! Detecting a black hole-neutron star ‘combined merger’
Everyone loves chocolate, and most of us cannot get sufficient peanut butter, however it’s when these two treats are combined that they actually come into their very own. It seems that black gap and neutron star mergers are the cosmic equal of chocolate peanut butter cups. No marvel scientists spent so lengthy looking for them.
On Jan. 5, 2020, LIGO/Virgo detected GW200105_162426, a sign from a neutron star with a mass 1.9 occasions that of the solar colliding with an 8.9-solar-mass black gap. It occurred 5 years after the detection of the primary black hole-black gap merger, and three years after the primary neutron star-neutron star merger.
This was the primary proof of a 3rd form of stellar remnant merger: a neutron star-black gap collision, or a “combined merger.” With peanut butter cups, one is never sufficient, and that seems to be true for combined mergers, too.

The second neutron star-black gap collision occasion was noticed within the type of the sign GW200115_042309, detected just some days afterward Jan. 15, 2020. This neutron star had an estimated mass 1.5 occasions that of the solar, with its companion being a 5.7-solar-mass black gap.
“With this new discovery of neutron star-black gap mergers exterior our galaxy, now we have discovered the lacking sort of binary,” Astrid Lamberts, a scientist with the French nationwide analysis company CNRS at Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur, mentioned in 2021. “We will lastly start to grasp what number of of those methods exist, how usually they merge, and why now we have not but seen examples within the Milky Manner.”
Up to now, the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA collaboration has detected and confirmed simply two combined mergers between a neutron star and a black gap, although there’s one other attainable candidate that hasn’t been absolutely vetted but.
7. The lightest black gap merger is a combined thriller
On Aug. 14, 2019, LIGO and Virgo detected the gravitational wave sign GW190814 from a merger that occurred 790 million light-years away.
Whereas one of many objects concerned was a black gap of twenty-two to 24 photo voltaic plenty, the identification of the second object is not as clear-cut as within the case of the combined mergers above. That is as a result of its mass is true within the candy spot between black holes and neutron stars.
With a mass 2.6 occasions that of the solar, the opposite element of this merger was both one of many lightest black holes ever seen or one of many heaviest neutron stars. As such, the truth that it was detected sooner than the 2 2020 alerts signifies that GW190814 may really be the primary recorded combined merger.
The merger stays shrouded in thriller. Astronomers can discover no electromagnetic counterpart, which means this may very well be two merging black holes or a black gap that has fully devoured a neutron star. Fixing this puzzle may assist us higher perceive the cycle of life and loss of life skilled by essentially the most huge stars.
8. This one goes as much as 11: The loudest gravitational wave ever!
Proving that the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA collaboration remains to be on the chopping fringe of gravitational wave science, this entry on our listing comes from simply this month!
On Sept. 10, 2025, LKV staff members introduced the detection of GW250114, the results of two merging black holes with plenty round 32 occasions the mass of the solar.
What makes GW250114 outstanding is the truth that it is likely one of the clearest gravitational wave alerts ever. So clear, in truth, that it not solely additional confirmed the idea of normal relativity but in addition verified the theories of different black gap luminaries.
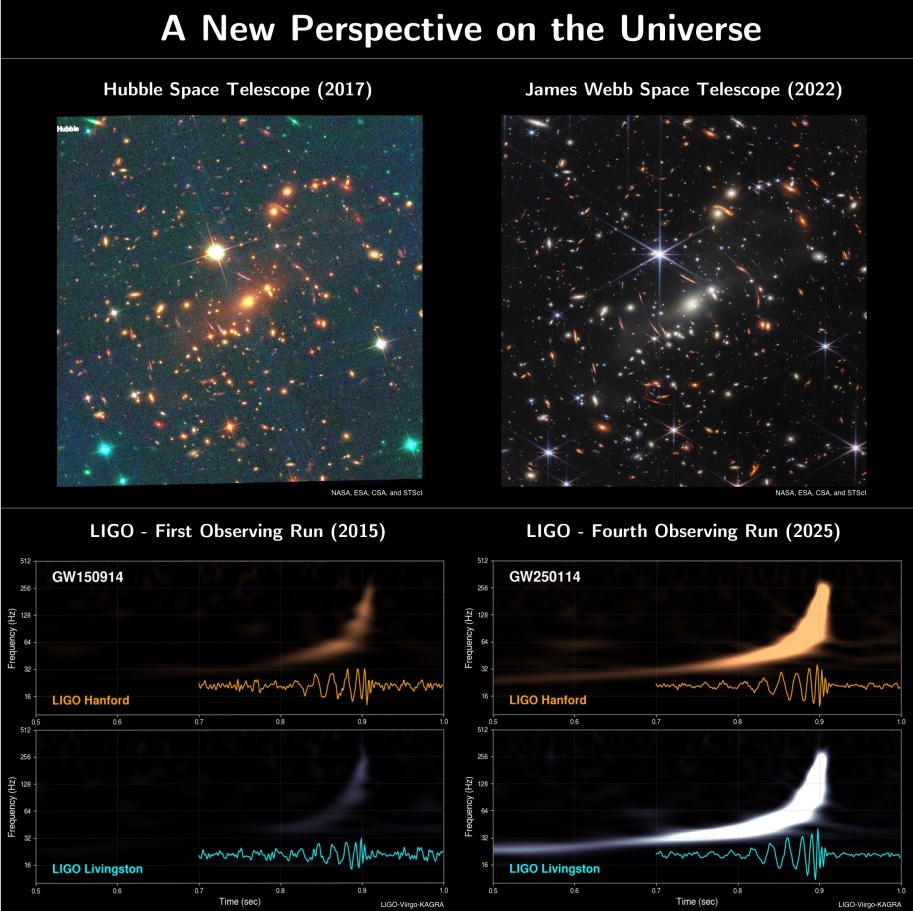
“GW250114 is the loudest gravitational wave occasion now we have detected thus far; it was like a whisper turning into a shout.” Geraint Pratten, member of the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA collaboration and a researcher on the College of Birmingham in England, mentioned in a assertion. “This gave us an unprecedented alternative to place Einstein’s theories by a few of the most rigorous assessments attainable — validating certainly one of Stephen Hawking’s pioneering predictions that when black holes merge, the mixed space of their occasion horizons can solely develop, by no means shrink.”
GW250114 will get on the listing as a result of it demonstrates simply how far LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA has come during the last 10 years.
Learn Extra: Gravitational wave detector confirms theories of Einstein and Hawking: ‘That is the clearest view but of the character of black holes’
9. Listening to a cosmic symphony
This one is not LVK-related, however it’s a gravitational wave discovery made over the last 10 years, so it nonetheless makes the listing.
On June 28, 2023, it was revealed that the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav) had detected low-frequency gravitational waves, a historic breakthrough that represents 15 years of looking. NANOGrav makes use of spinning neutron star pulsars as a timing array to detect the tiny fluctuations in space-time attributable to gravitational waves.
The gravitational waves detected by LIGO and its collaborators signify a dramatic single “crash” of cymbals from violent occasions like collisions and mergers; the low-frequency gravitational wave sign NANOGrav heard is extra akin to the light background concord of violins.
The power of the sign represents a gravitational wave orchestra of tons of of hundreds, perhaps even thousands and thousands, of supermassive black holes swirling round one another and finally merging within the early universe.
“This discovering opens up a brand new low-frequency window on the gravitational universe which is able to allow us to examine how galaxies and their central black holes merge and develop with time,” Nationwide Radio Astronomy Observatory astronomer and NANOGrav researcher Scott Ransom informed Area.com in 2023.
10. Proving Einstein … fallacious!?!

This will come as a little bit of shock, however whereas each gravitational wave discovery made since 2015 has verified Einstein’s idea of normal relativity, mockingly, every has additionally proved the good physicist fallacious, too.
That is as a result of Einstein believed that gravitational waves are so faint and so insubstantial, when it comes to the displacement of space-time they trigger as they wash by the cosmos at close to light-speed, that we’d by no means be capable to detect them.
Even a few of the scientists who have been integral to the event of LIGO and the primary detection of gravitational waves weren’t initially sure such a feat was attainable, agreeing with Einstein.
“Rai Weiss proposed the idea of LIGO in 1972, and I assumed, ‘This does not have a lot probability in any respect of working,'” Kip Thorne, an knowledgeable on the idea of black holes, mentioned in a assertion earlier this month. “We needed to invent an entire new expertise.”

