A weak spot in Earth’s magnetic area over the South Atlantic Ocean has ballooned in measurement since 2014, satellite tv for pc knowledge reveals.
The area, referred to as the South Atlantic Anomaly, has grown by an space almost half the dimensions of continental Europe, sprouting a lobe within the path of Africa the place the sphere is weakening the quickest.
“The South Atlantic Anomaly isn’t just a single block,” examine lead creator Chris Finlay, a professor of geomagnetism on the Technical College of Denmark, mentioned in a assertion. “It is altering in a different way in direction of Africa than it’s close to South America. There’s one thing particular taking place on this area that’s inflicting the sphere to weaken in a extra intense means.”
Researchers first detected the South Atlantic Anomaly within the nineteenth century. Inside its boundaries, the magnetic area that radiates away from Earth’s inside dips all the way down to an altitude of about 120 miles (200 kilometers) above the planet’s floor, which is way decrease than the sphere’s common altitude of about 400 miles (650 km).
This poses a risk to satellites and different spacecraft. Earth’s magnetic area shields the planet and objects in low Earth orbit from charged photo voltaic particles and incoming X-ray and ultraviolet radiation, so spacecraft touring over the South Atlantic Anomaly are uncovered to extra of those impacts. This might result in malfunctions or injury in {hardware}, and even blackouts, in line with the assertion.
Finlay and his colleagues assume the South Atlantic Anomaly is rising and spreading eastward as a result of unusual fluxes on the restrict between Earth’s mantle and outer core, the layers of the planet sandwiched between Earth’s crust and inside core.
Earth’s magnetic area is essentially generated by Earth’s outer core — an ocean of swirling, molten iron positioned roughly 1,900 miles (3,000 km) beneath the planet’s floor. The liquid iron dynamo generates electrical currents, and their circulate induces a magnetic area that spreads up into the mantle and extends by Earth’s environment, forming two big rings that be part of close to the poles.
Scientists beforehand discovered that in some areas beneath the South Atlantic Anomaly, the magnetism generated by the outer core is looping again into the core as an alternative of popping out. These patterns, referred to as reverse flux patches, can migrate and broaden, explaining the expansion of the South Atlantic Anomaly over the previous 11 years, Finlay mentioned.
“We are able to see one in every of these areas shifting westward over Africa, which contributes to the weakening of the South Atlantic Anomaly [the magnetic field] on this area,” he added.
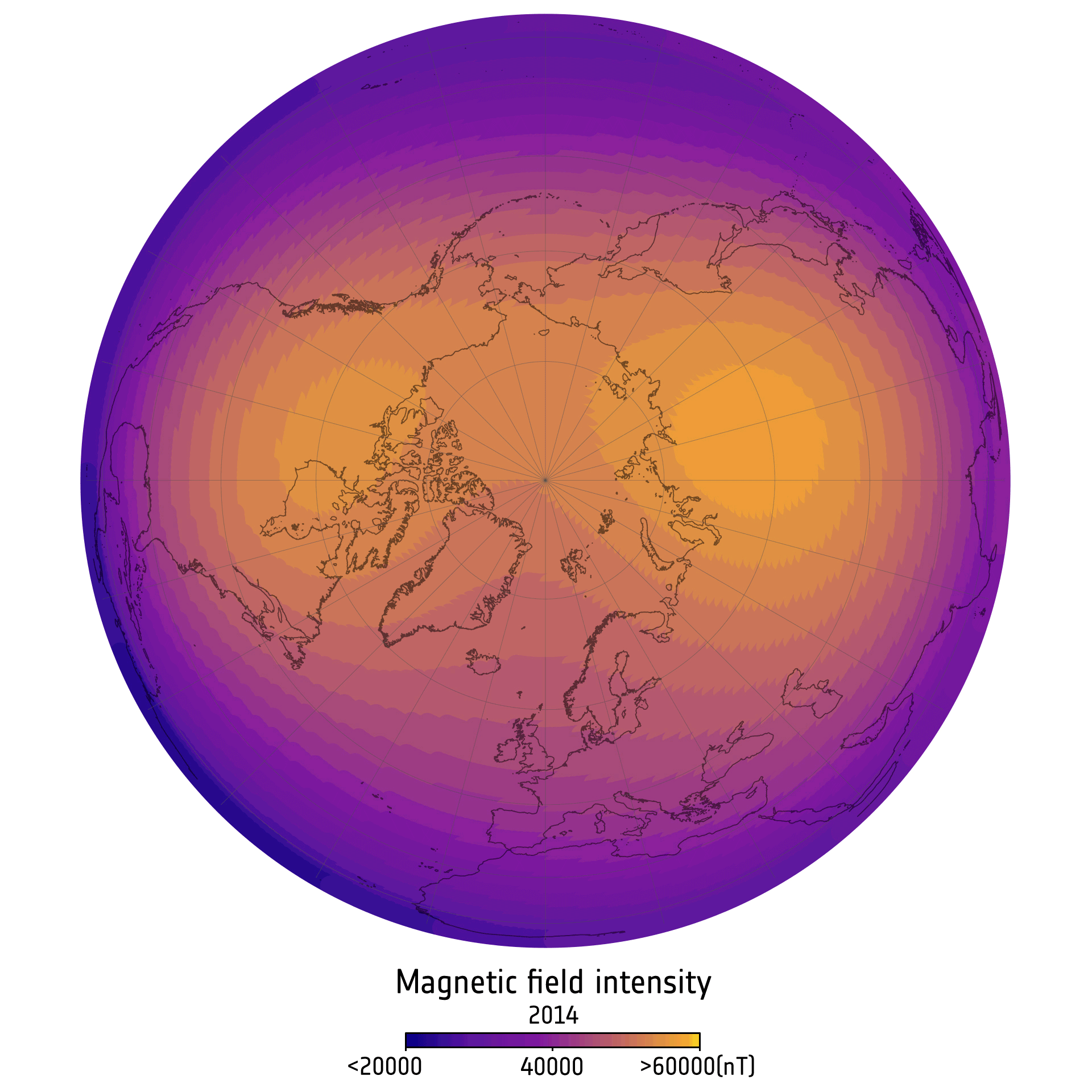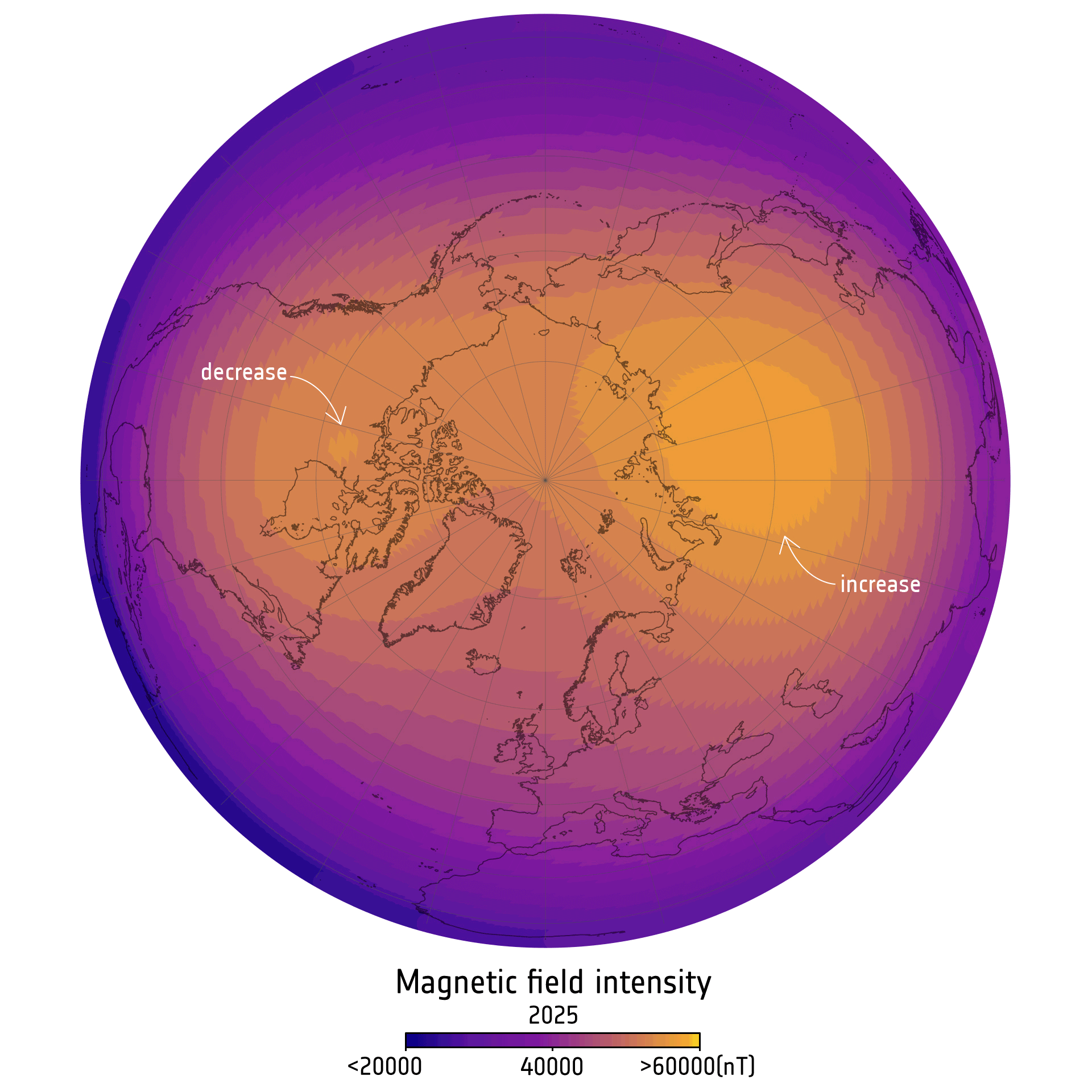
The scientists noticed the weird shifts in knowledge from the European House Company’s (ESA’s) ongoing Swarm mission, which makes use of three equivalent satellites to measure magnetic indicators originating from Earth’s inside and oceans. The information additionally revealed adjustments in magnetic area dynamics above Canada and Siberia, the place magnetism has appeared extra intense than common since Swarm started its observations in 2013.
Since 2014, the magnetic area above Canada has weakened barely, and the magnetic area above Siberia has strengthened, the brand new examine reveals. The robust area over Canada has shrunk by an space almost the dimensions of India, whereas the robust area over Siberia has grown by an space the dimensions of Greenland. The researchers attributed these adjustments to a shift in Earth’s northern magnetic pole in Siberia’s path over latest years, however extra monitoring is required to see how the dynamics evolve.
“It is actually great to see the large image of our dynamic Earth,” Anja Strømme, ESA’s Swarm mission supervisor, mentioned within the assertion. “The satellites are all wholesome and offering glorious knowledge, so we will hopefully lengthen that report past 2030.”

