Artemis 2 astronauts shall be studied for a way sleep, stress and radiation form human well being in deep house throughout their moon mission subsequent 12 months.
The second installment of NASA’s Artemis program to return to the moon and set up a sustained human presence in deep house is ready to be the primary crewed flight check of its Orion spacecraft and Area Launch System (SLS) rocket. The four-person crew is tasked with placing the vessel by means of its paces within the cislunar setting, and performing a number of science experiments throughout their mission.
A few of that analysis entails the astronauts themselves, who will flip right into a quartet of biomedical topics to assist NASA collect in-flight information on the human physique past low Earth orbit for the primary time in additional than 50 years. As they’ve with lots of of physiological assessments performed aboard the Worldwide Area Station (ISS), NASA will add the analysis to its rising understanding of the organic repercussions of life in microgravity, in accordance with a current launch.
Customary measures
One of many experiments the Artemis 2 astronauts will undertake will see them be part of a long-running NASA effort to construct a complete understanding of how spaceflight impacts human well being. Samples of blood, urine and saliva are being collected within the months earlier than launch, and the astronauts will endure common checks throughout their 10-day mission and follow-ups after their return.
NASA hopes to make use of the samples to trace adjustments in cardiovascular well being, vitamin, immunity and stress throughout a number of phases of coaching, flight and restoration.
ARCHeR: Sleep and stress monitoring
The Artemis Analysis for Crew Well being and Readiness (ARCHeR) challenge will examine how crew efficiency may be affected by time spent as such a far distance from Earth whereas inside Orion’s confined house, mixed with the astronauts’ demanding schedule.
Every Artemis 2 astronaut will put on wrist sensors to log motion and sleep all through the mission. Pre- and post-mission evaluations shall be in comparison with in-flight information to higher perceive how the deep house mission influences the crew’s alertness, stress and skill to work collectively cohesively.
Immune system monitoring
Samples supplied by the crew earlier than, throughout and after their mission may also be used to check their immune techniques. On this case, immune system markers of their saliva samples will assist researchers consider how the physique reacts to house radiation.
To save lots of house and energy aboard Orion throughout their mission, the crew is foregoing refrigeration of their in-flight saliva samples, and can as an alternative make their deposits on specifically designed dab papers, which is able to soak up the samples for easier storage. As soon as they return, scientists will check the papers for dormant viruses triggered by the microgravity setting — a phenomenon seen aboard the ISS, the place stress has been documented as a set off to reactivate sicknesses like chickenpox and shingles.
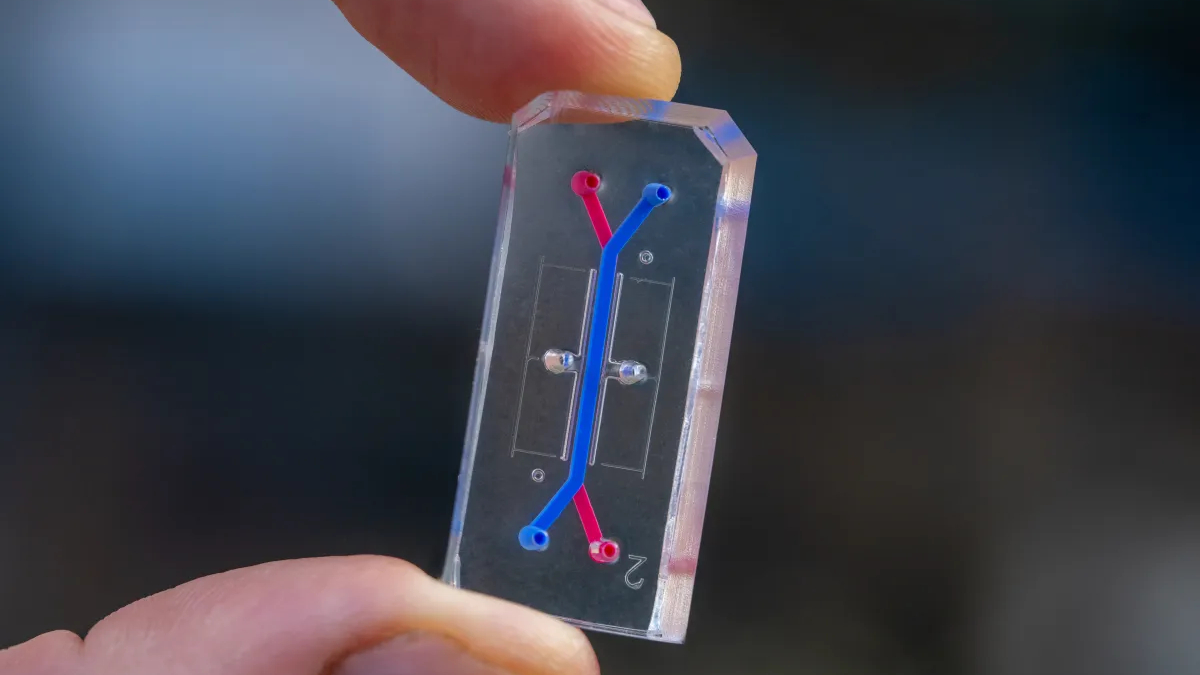
AVATAR organ-on-a-chip research
Artemis 2 astronauts may also be accompanied by thumb-sized “avatars” of themselves, within the type of blood samples grown to simulate bone marrow on organ-on-a-chip gadgets.
These chips will journey inside Orion because it passes by means of the Van Allen belts — zones of charged particles between the Earth and moon — testing how marrow responds to deep house radiation and microgravity. Outcomes shall be in comparison with ISS experiments to see if the chip know-how can precisely predict how tissues react exterior Earth’s radiation-hardened magnetosphere.
Radiation
The gadgets will measure the constant radiation publicity skilled all through the mission, and detect sudden spikes from issues like photo voltaic storms. If readings attain harmful ranges, astronauts can assemble a makeshift radiation protect inside Orion, fortifying themselves between the spacecraft’s heatshield and water storage canisters, each of that are higher at absorbing penetrating radiation than different onboard supplies.
NASA has chosen Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Area Company) astronaut Jeremy Hansen because the crew for the Artemis 2 mission. They’re scheduled to launch no sooner than Feb. 2026, with a launch window that extends by means of April.

