[ad_1]
This text was initially revealed at The Dialog. The publication contributed the article to Area.com’s Skilled Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
Think about a digicam so highly effective it will probably see mild from galaxies that shaped greater than 13 billion years in the past. That’s precisely what NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope is constructed to do.
Because it launched in December 2021, Webb has been orbiting greater than 1,000,000 miles from Earth, capturing breathtaking pictures of deep house. However how does it really work? And the way can it see up to now? The key lies in its highly effective cameras – particularly ones that don’t see mild the way in which our eyes do.
I’m an astrophysicist who research galaxies and supermassive black holes, and the Webb telescope is an unimaginable device for observing a few of the earliest galaxies and black holes within the universe.
When Webb takes an image of a distant galaxy, astronomers like me are literally seeing what that galaxy appeared like billions of years in the past. The sunshine from that galaxy has been touring throughout house for the billions of years it takes to achieve the telescope’s mirror. It’s like having a time machine that takes snapshots of the early universe.
By utilizing a large mirror to gather historical mild, Webb has been discovering new secrets and techniques concerning the universe.
A telescope that sees warmth
In contrast to common cameras and even the Hubble Area Telescope, which take pictures of seen mild, Webb is designed to see a type of mild that’s invisible to your eyes: infrared mild. Infrared mild has longer wavelengths than seen mild, which is why our eyes can’t detect it. However with the appropriate devices, Webb can seize infrared mild to check a few of the earliest and most distant objects within the universe.
Though the human eye can not see it, folks can detect infrared mild as a type of warmth utilizing specialised expertise, akin to infrared cameras or thermal sensors. For instance, night-vision goggles use infrared mild to detect heat objects at the hours of darkness. Webb makes use of the identical concept to check stars, galaxies and planets.
Why infrared? When seen mild from faraway galaxies travels throughout the universe, it stretches out. It’s because the universe is increasing. That stretching turns seen mild into infrared mild. So, essentially the most distant galaxies in house don’t shine in seen mild anymore – they glow in faint infrared. That’s the sunshine Webb is constructed to detect.
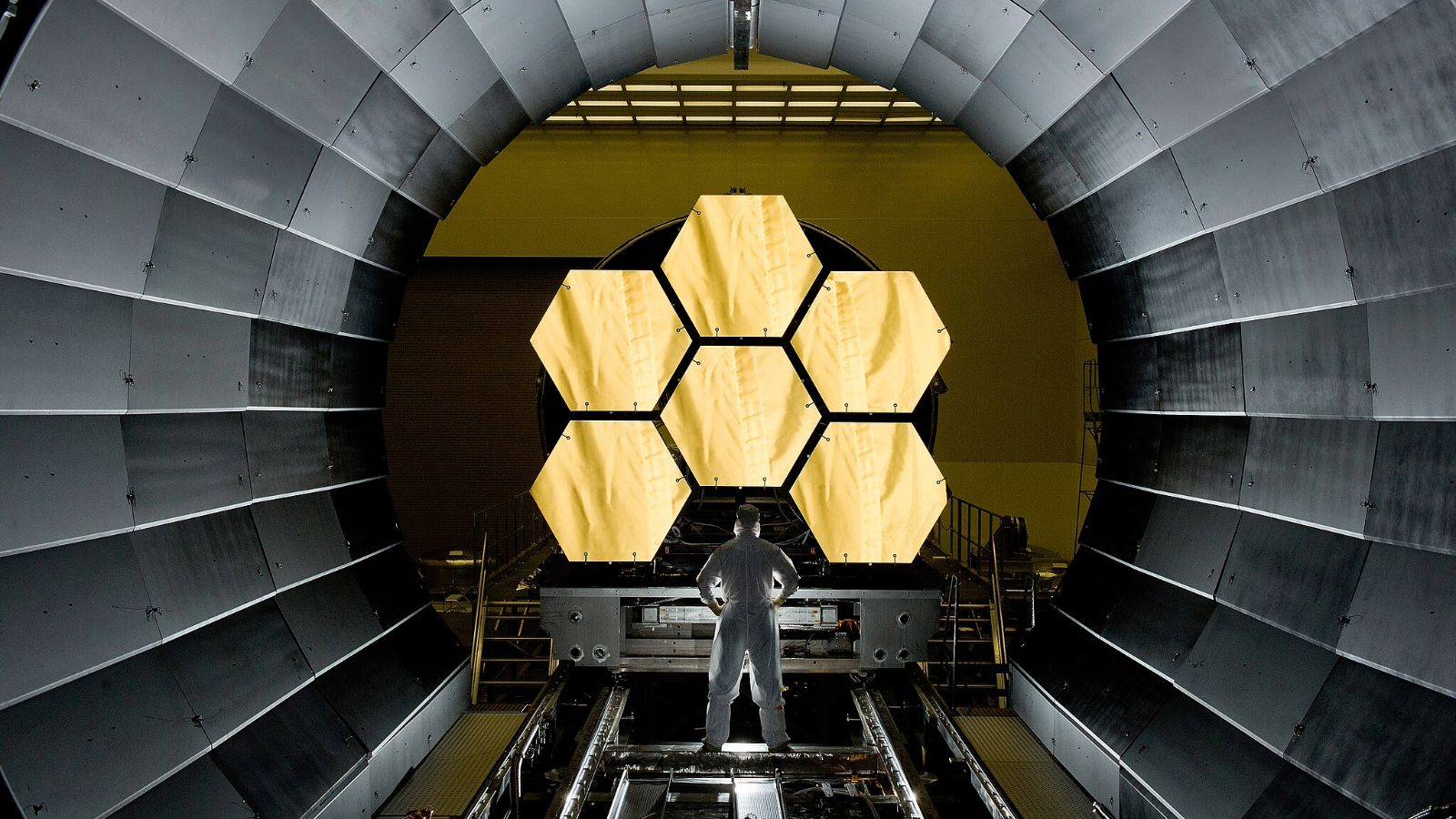
A golden mirror to collect the faintest glow
Earlier than the sunshine reaches the cameras, it first needs to be collected by the Webb telescope’s monumental golden mirror. This mirror is over 21 ft (6.5 meters) extensive and fabricated from 18 smaller mirror items that match collectively like a honeycomb. It’s coated in a skinny layer of actual gold – not simply to look fancy, however as a result of gold displays infrared mild extraordinarily nicely.
The mirror gathers mild from deep house and displays it into the telescope’s devices. The larger the mirror, the extra mild it will probably acquire – and the farther it will probably see. Webb’s mirror is the biggest ever launched into house.

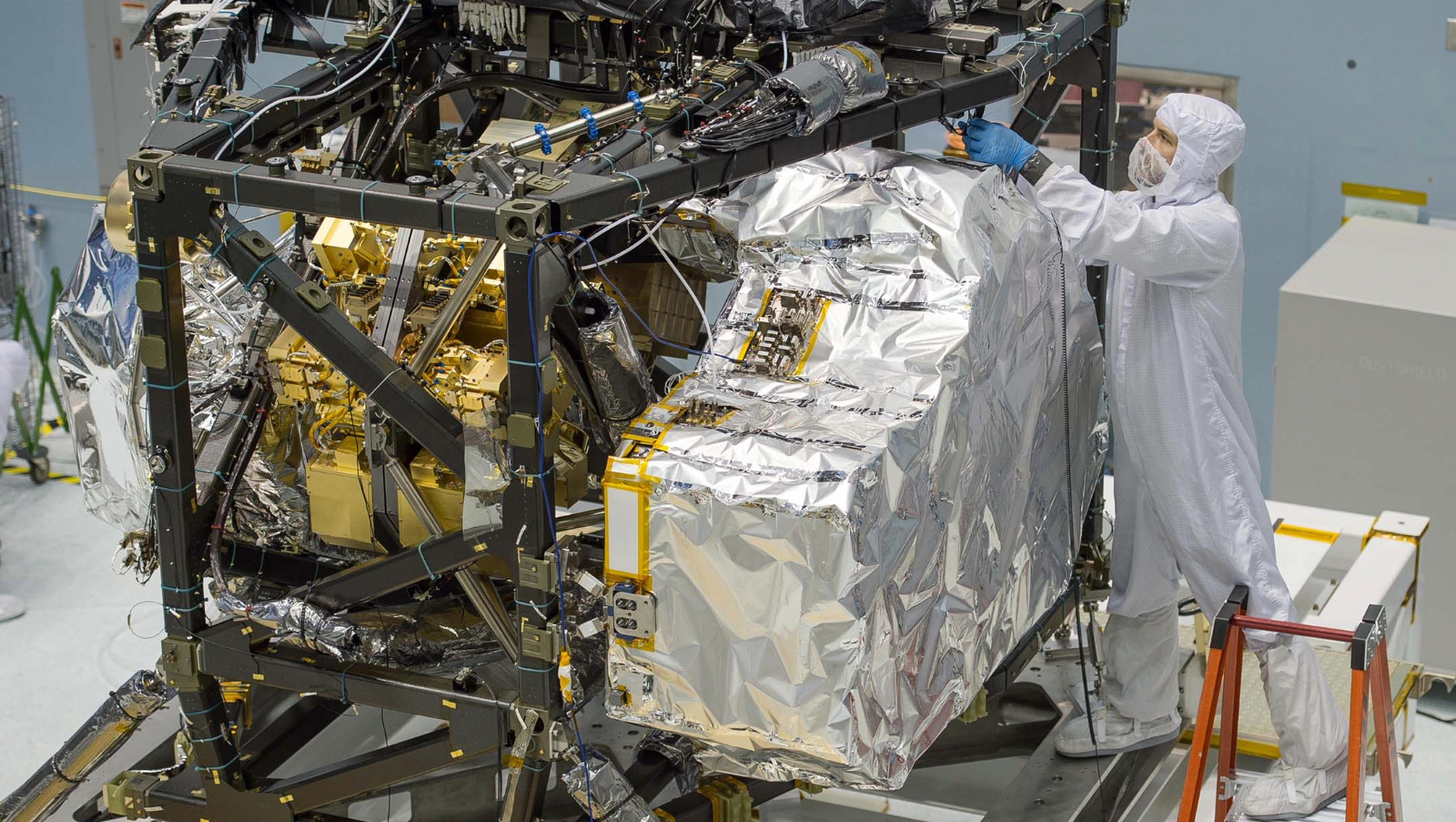
Contained in the cameras: NIRCam and MIRI
An important “eyes” of the telescope are two science devices that act like cameras: NIRCam and MIRI.
NIRCam stands for near-infrared digicam. It’s the first digicam on Webb and takes beautiful pictures of galaxies and stars. It additionally has a coronagraph – a tool that blocks out starlight so it will probably {photograph} very faint objects close to shiny sources, akin to planets orbiting shiny stars.
NIRCam works by imaging near-infrared mild, the sort closest to what human eyes can virtually see, and splitting it into completely different wavelengths. This helps scientists be taught not simply what one thing seems like however what it’s fabricated from. Totally different supplies in house soak up and emit infrared mild at particular wavelengths, making a type of distinctive chemical fingerprint. By finding out these fingerprints, scientists can uncover the properties of distant stars and galaxies.
MIRI, or the mid-infrared instrument, detects longer infrared wavelengths, that are particularly helpful for recognizing cooler and dustier objects, akin to stars which are nonetheless forming inside clouds of gasoline. MIRI may even assist discover clues concerning the kinds of molecules within the atmospheres of planets which may help life.
Each cameras are much more delicate than the usual cameras used on Earth. NIRCam and MIRI can detect the tiniest quantities of warmth from billions of light-years away. When you had Webb’s NIRCam as your eyes, you may see the warmth from a bumblebee on the Moon. That’s how delicate it’s.

As a result of Webb is making an attempt to detect faint warmth from faraway objects, it must preserve itself as chilly as attainable. That’s why it carries a large solar protect concerning the measurement of a tennis court docket. This five-layer solar protect blocks warmth from the Solar, Earth and even the Moon, serving to Webb keep extremely chilly: round -370 levels F (-223 levels C).
MIRI must be even colder. It has its personal particular fridge, known as a cryocooler, to maintain it chilled to just about -447 levels F (-266 levels C). If Webb have been even somewhat heat, its personal warmth would drown out the distant alerts it’s making an attempt to detect.
Turning house mild into footage
As soon as mild reaches the Webb telescope’s cameras, it hits sensors known as detectors. These detectors don’t seize common images like a cellphone digicam. As an alternative, they convert the incoming infrared mild into digital knowledge. That knowledge is then despatched again to Earth, the place scientists course of it into full-color pictures.
The colours we see in Webb’s footage aren’t what the digicam “sees” immediately. As a result of infrared mild is invisible, scientists assign colours to completely different wavelengths to assist us perceive what’s within the picture. These processed pictures assist present the construction, age and composition of galaxies, stars and extra.
By utilizing a large mirror to gather invisible infrared mild and sending it to super-cold cameras, Webb lets us see galaxies that shaped simply after the universe started.
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the unique article.
[ad_2]

