[ad_1]
New Interstellar Object Stuns Scientists as It Zooms by means of Photo voltaic System
All eyes are on Comet 3I/Atlas as astronomers worldwide chase the unique ice ball by means of our photo voltaic system
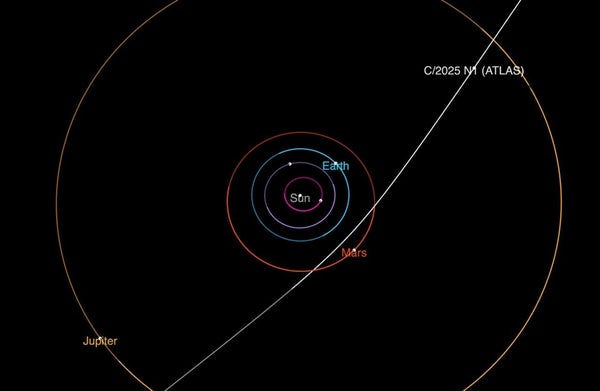
A diagram exhibits the trajectory of interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS because it passes by means of the photo voltaic system. It can make its closest method to the solar in October.
Late within the night on July 1, a telescope in Chile that’s a part of the worldwide, NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-Impression Final Alert System (ATLAS) picked up on a brand new transferring dot within the sky, an object touring previous the orbit of Jupiter. When Larry Denneau, a software program engineer at ATLAS, alerted the Worldwide Astronomical Union’s Minor Planet Heart to the remark, “it appeared like a totally routine discovery,” he says. That might quickly change. To his shock, the article—provisionally named A11pI3Z—turned out to be the third interstellar customer recognized to science.
Now, mere days after its discovery, frenzied follow-up work by astronomers world wide to additional scrutinize A11pI3Z and search for extra apparitions in archival observations has given the article a brand new, extra official title—Comet 3I/Atlas—for the telescope that first found it. What appears to have been the clinching proof for its interstellar nature emerged from the efforts of a bunch of newbie astronomers, known as the Deep Random Survey, who have been the primary to trace the article down in photos different ATLAS telescopes had captured in late June.
“We had fairly a little bit of confusion from the get-go,” says Sam Deen, a member of the group. “Our techniques are normally tuned to count on {that a} new discovery is an object firmly caught contained in the photo voltaic system,” however Atlas was taking part in outdoors of these guidelines. The sooner observations—which quickly additionally included “prediscovery” sightings from the Zwicky Transient Facility on the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, in addition to different telescopes—allowed a extra exact calculation of 3I/Atlas’s trajectory. No matter it was, the article was zooming towards the internal photo voltaic system at virtually 70 kilometers per second.
On supporting science journalism
When you’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you’re serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world immediately.
That’s “far sooner than any photo voltaic system object ought to have the ability to transfer,” Deen notes, as a result of such speeds guarantee objects will slip by means of the solar’s gravitational grasp. Something transferring so rapidly merely can’t hold round lengthy; moderately than following a typical parabolic orbit, 3I/Atlas’s blistering pace is carving out a hyperbolic orbit, a path that takes the article swooping by means of the internal photo voltaic system earlier than it soars again to the interstellar void. It more than likely got here from the outskirts of another planetary system, the place it was ejected from its tenuous twirling round some alien solar by gravitational interactions with an enormous planet or one other passing star. Precisely the place it got here from and when it started its galactic journey, nevertheless, nobody can say.
There is no such thing as a risk to Earth: throughout its transient sojourn within the photo voltaic system 3I/Atlas is projected to return no nearer than about 240 million kilometers from our planet. The item will make its closest method to the solar on October 30, reaching a distance of about 210 million kilometers, simply inside the orbit of Mars. Because it approaches in coming months, astronomers will intensify their research, hoping to be taught extra about this mysterious customer.
What’s already comparatively clear, nevertheless, is 3I/Atlas’s cometary nature; greater than 100 observations have now trickled in from telescopes across the globe, together with some that present hints the article is enveloped in a cloud of gasoline and dirt and trailing a tail of particles as ices on its floor heat within the solar’s radiance. Astronomers usually use a distant object’s brightness as a proxy for its dimension, with brighter objects tending to be greater as effectively. However a comet’s ejected materials is normally brilliant, too, which interferes with such crude estimates.
Consequently, “proper now we actually do not understand how huge it’s; it may very well be wherever from 5 to 50 kilometers in diameter,” Denneau says. Nearer seems to be with extra highly effective observatories, together with the keen-eyed, infrared James Webb House Telescope, ought to quickly assist make clear 3I/Atlas’s dimensions and composition.
“I’m involved in whether or not the comet seems to be like objects from our personal photo voltaic system,” Denneau says. “The reply is fascinating both means. If it has the identical composition as a standard comet, it implies that different photo voltaic techniques could also be constructed equally to ours. If it’s utterly completely different, then we would surprise why that’s.”
The primary interstellar object noticed, 1I/‘Oumuamua, appeared on the scene in 2017 and perplexed researchers with its oddly elongated form and bizarrely accelerating trajectory. These unusual options led some researchers to suggest an thought—now convincingly debunked—that ‘Oumuamua was a derelict alien spacecraft adrift within the Milky Approach. Then, in 2019, got here the second noticed interstellar object, 2I/Borisov, which bore all of the hallmarks of a run-of-the-mill comet and thus impressed few, if any, outlandish claims of alien involvement.
“[ATLAS] shall be a tiebreaker of types,” says Mario Jurić, an astronomer on the College of Washington and discovery software program lead on the not too long ago accomplished Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile. “[Will it] give us a way ‘Oumuamua was the odd one out, or is the universe much more fascinating than we imagined?”
Rubin—a novel telescope with a panoramic view that can survey your entire overhead sky each few days—is seen as particularly crucial for fixing the lingering mysteries of those first emissaries from interstellar house. Because the observatory’s survey progresses in months and years to return, it ought to uncover many extra guests from the nice past, permitting astronomers to start finding out them as a inhabitants moderately than scattered, remoted one-offs.
Finally, if Rubin or one other facility manages to identify an interstellar object fortuitously poised to cross comparatively near Earth, astronomers may even have the ability to achieve a particularly close-up view by way of a spacecraft rendezvous. The European House Company (ESA) already has such a mission within the works, in actual fact—Comet Interceptor, a sentinel spacecraft set to launch as early as 2029 to await some inbound vacation spot. “There’s a small likelihood that Comet Interceptor may have the ability to go to an interstellar object if one is discovered on the correct trajectory, and the brand new Vera C. Rubin Observatory ought to give us an elevated charge of discovery of those objects,” says Colin Snodgrass, an astronomer on the College of Edinburgh, who’s a part of the ESA mission.
All of that has astronomers on the sting of their seat, desirous to dive deeper into a brand new frontier in our cosmic understanding. “That is in all probability essentially the most excited I’ve been about any astronomical discovery in years,” Deen says.
[ad_2]

