September’s new moon will partially eclipse the solar, although the eclipse will solely be seen from the southern Pacific Ocean and Antarctica.
A new moon is when the moon shares the identical celestial longitude as the solar; the 2 our bodies are mentioned to be in conjunction. This happens about each 29.5 days. The precise second of this months’ new moon happens in the present day (Sept. 21) at 3:54 p.m. EDT (1954 GMT).
This additionally places the moon between the solar and Earth, and if the brand new moon is completely lined up with the solar, we see a photo voltaic eclipse. Photo voltaic eclipses aren’t seen from all over the place on Earth as a result of the moon’s shadow solely covers a small a part of the Earth’s floor, so whereas photo voltaic eclipses occur about twice a 12 months, a given level on Earth will probably be within the moon’s shadow rather a lot much less typically.
Photo voltaic eclipses will be both partial or whole; this one is a partial eclipse so solely a portion of the solar is roofed by the moon; the solar seems to be a crescent or to have a “chew” taken out of it. One must be very cautious observing photo voltaic eclipses; use of eclipse glasses or specialised photo voltaic filters is a should; and by no means have a look at the solar by means of any form of optical assist (corresponding to a digicam lens, binoculars or telescope) with no filter; the end result will be everlasting blindness from retinal burns.
On this case, the bounds of the partial eclipse visibility extends from the southern atolls of Kiribati and Fiji within the north, French Polynesia and the Antarctic Peninsula within the east, and the jap coasts of Australia and Tasmania within the west, (although Australians and Tasmanians will solely see a tiny sliver of the solar coated). Southern New Zealand permits for observing the deepest eclipse; one can accomplish that from the southern half of Stewart Island.
Oban, New Zealand, is the one city on Stewart Island, and there the eclipse begins at 6:10 a.m. New Zealand Normal Time on Sept. 22. Dawn in Oban is at 6:37 a.m., so the eclipse begins whereas the solar is under the horizon. Because the solar rises, one will see a crescent because the moon is already protecting the upper-left portion of the solar. Most eclipse happens at 7:14 a.m. – the solar will nonetheless be solely about 6 levels excessive within the east – and the eclipse ends at 8:23 a.m. About 73 % of the solar’s disk will probably be coated at most eclipse.
In much less distant elements of New Zealand corresponding to Christchurch, as much as 69 % of the solar will probably be coated. As in Oban, the eclipse begins at 6:03 a.m., earlier than the solar rises at 6:19 a.m. At that time the moon is protecting a small a part of the upper-left facet of the solar (the northern facet). Most eclipse is at 7:08 a.m. native time, and the moon will seem to have shifted to the opposite facet of the solar even because it covers extra of it; one will be capable of see the “Satan horns” form because the solar will seem like a crescent with the factors dealing with upwards. The eclipse ends at 8:18 a.m.
For observers in Fiji, solely about 27 % of the solar will probably be coated; in Suva (the biggest metropolis) the eclipse begins Sept. 22 at 5:31 a.m. native time (earlier than dawn). Dawn is at 5:56 a.m. and the highest a part of the solar will probably be obscured; the utmost eclipse is at 6:22 a.m. and the eclipse ends at 7:19 a.m.
Seen planets
For these that may’t see the eclipse, the evening of the brand new moon gives some seen planets, every following the opposite within the sky because the evening progresses. In New York Metropolis (different places in mid-northern latitudes could have comparable occasions) sundown on Sept. 21 – the day earlier than the equinox – is at 6:54 p.m. EDT. The tip of civil twilight, when the sky will get darkish sufficient that streetlights start to activate, is at 7:21 p.m. If one is close to a flat, unobstructed horizon and has a transparent sky, it is simply doable to catch Mars, which will probably be solely about 7 levels excessive within the southwest. The planet is not vibrant sufficient to be very distinct towards the sky, so observing the planet earlier than it units at 8:05 p.m. EDT. The crimson planet will probably be way more seen later within the 12 months because it emerges from the solar’s glare within the evenings.
Jupiter rises subsequent, at 12:59 a.m. Sept. 22. Jupiter is within the constellation Gemini, the Twins, and will probably be to the fitting of the 2 brightest stars within the constellation, Castor and Pollux. Jupiter will probably be brighter than both of these two stars, which will probably be on the left facet of the planet. Jupiter transits at 8:22 a.m., so it will likely be misplaced in daylight earlier than it will get there, however by 6:00 a.m. the planet will probably be a full 54 levels excessive within the east-southeast.
After Jupiter we see Venus, which rises at 4:31 a.m. EDT on Sept. 22. Venus is the third brightest object within the sky after the solar and moon, so it will likely be fairly apparent even whether it is near the horizon. Dawn is at 6:44 a.m. EDT and Venus will probably be seen till about 6:30 a.m., when it will likely be about 21 levels excessive within the east.
Nearer the equator, some planets turn out to be simpler to see. In Bogota, Colombia, for instance, Mars units at 7:41 p.m. native time, and sundown is at 6:13 p.m. The planet continues to be about 16 levels above the western horizon by 6:30 p.m. when the sky is getting darkish, so it spends a bit longer out of the photo voltaic glare than in places additional north. Saturn, in the meantime, rises at 5:49 p.m. – nonetheless in daylight – and a couple of half hour after sundown is 13 levels excessive within the east. The planet transits at 11:49 p.m. and is 82 levels excessive—virtually straight overhead.
Jupiter rises at 1:13 a.m. native time on Sept. 22, and by 2:30 a.m. one can see it within the east about 17 levels above the horizon. Venus follows at 4:07 a.m. and is about 20 levels excessive within the east by 5:30 a.m. (dawn in Bogota is at 5:46 a.m.).
Southern Hemisphere places could have the simplest time recognizing Mars within the night. In Santiago, Chile, sundown on Sept. 21 is at 7:39 p.m. native time and civil twilight ends at 8:03 p.m. Mars units at 10:02 p.m. so by 8:15 p.m. it can nonetheless be about 21 levels excessive within the west.
Because the sky will get darkish, Saturn will probably be within the east; the ringed planet rises at 7:26 p.m. – earlier than sundown – however by 8:30 p.m. Saturn is 12 levels above the jap horizon. The planet transits at 1:36 a.m. Sept. 22, and will probably be 59 levels excessive within the north; practically two thirds of the best way to the zenith.
Jupiter rises in Santiago at 4:07 a.m. on Sept. 22 and from mid-southern latitudes it can seem like above and to the fitting of Castor and Pollux, with Pollux showing virtually straight under the planet. By 5:30 a.m. it’s 14 levels excessive within the northeast.
Venus rises at 6:27 a.m., so it is just seen for a short while – dawn is at 7:22 a.m. and the planet is barely 10 levels excessive by then; vibrant as it’s it will likely be troublesome to identify with no clear and unobstructed horizon.
Constellations
In late September, by about 8:30 p.m., one can look virtually due west to see Arcturus, a vibrant orange-white star, about 20 levels excessive. Arcturus is recognizable due to its coloration – it could possibly look distinctly orange, and from mid-northern latitudes Mar has already set, so there is no complicated the 2. If one appears to be like to the fitting, in direction of the north, one will see the Large Dipper, the asterism that’s a part of Ursa Main, the Nice Bear.
Trying to the left of Arcturus (barely southward) and upwards, one can see a vibrant star that’s the heart of a small arc of fainter stars; that is the constellation Corona Borealis, the Northern Crown, and its vibrant star known as Alphecca.
Going again to the Large Dipper, which can look virtually horizontal, one can use the “pointers” — the 2 stars on the entrance of the bowl (the fitting facet) to search out Polaris, the Pole Star. The pointers are known as Dubhe and Merak, with Dubhe being the one nearer to Polaris. Polaris will probably be upwards; and from a darker-sky location one can see to the left of Polaris the 2 fainter stars known as the Guardians, that are one facet of the bowl of the Little Dipper. The decrease one known as Kochab and the higher one Pherkad.
If one continues the road from the Dipper by means of Polaris, one sees Cepheus, the legendary king of Aethiopia. Slightly below that’s the “W” form that represents Queen Cassiopeia, his spouse. Each are in direction of the northeast and comparatively excessive within the sky; about midway to the zenith. Cassiopeia, Cepheus, and the Large Dipper are all referred to as circumpolar stars – they by no means really set for a lot of Northern Hemisphere observers. As one strikes northwards, extra of the southern stars transfer under the horizon and are not seen in any respect, however extra of the constellations within the northern half of the sky turn out to be circumpolar. The identical is true as one strikes into the Southern Hemisphere, although it’s the northern stars that go under the horizon and a distinct set of constellations that turn out to be circumpolar.
Trying additional eastwards and in direction of the horizon, utilizing the pointed elements of the “W” one can see a protracted arc of 4 medium-bright stars that kind a part of the constellation Andromeda, Cassiopeia’s daughter. The rightmost level of the arc (it appears to be like like a protracted smile) is a part of the Nice Sq., which can seem like it’s standing on one nook. That sq. is the wing of Pegasus, the winged horse.
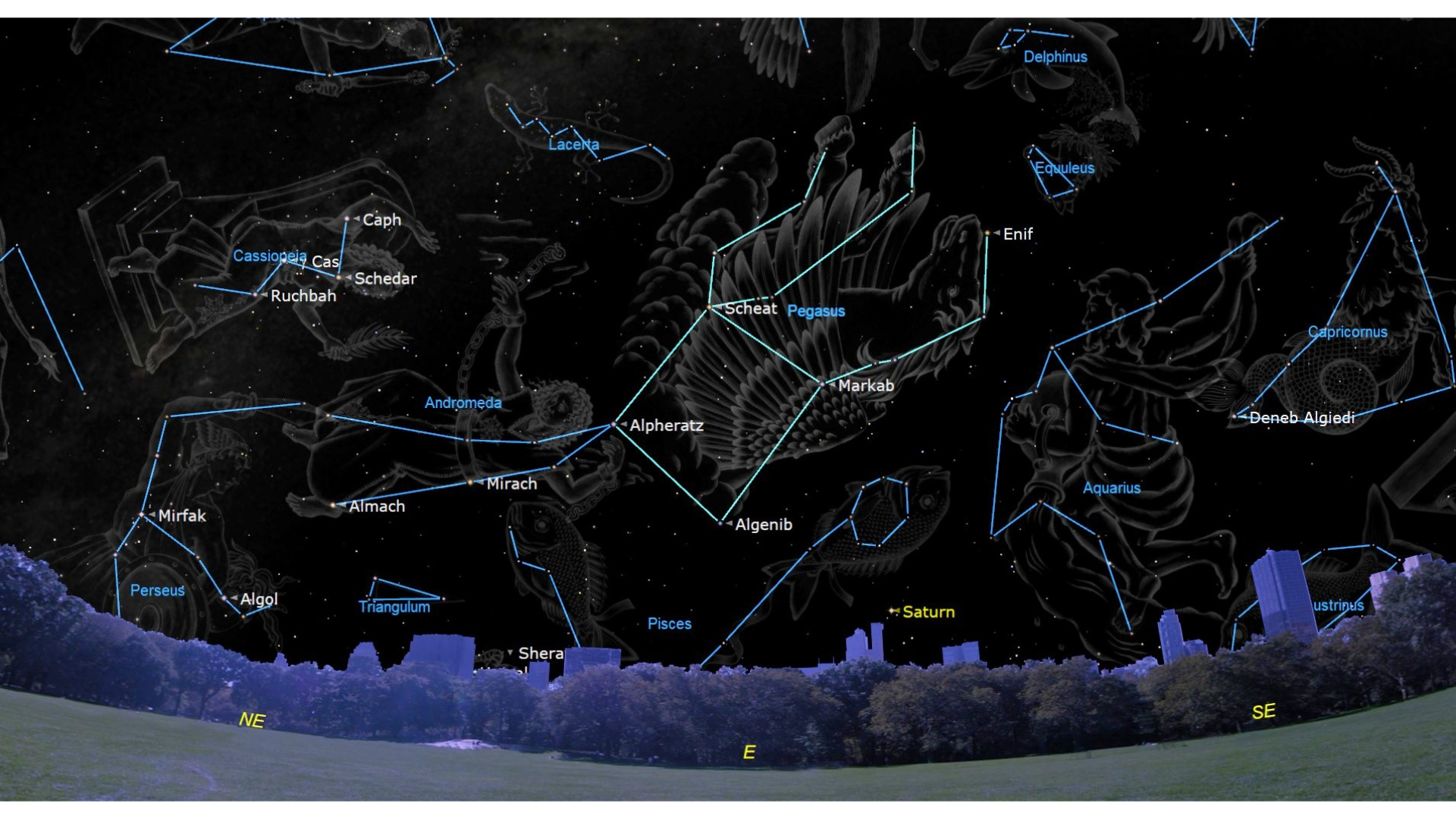
On this evening the Summer season Triangle – an asterism made up of Deneb, Altair and Vega – is sort of straight overhead. It is recognizable because the three stars are vibrant sufficient to see even in a metropolis location; Altair, the “eye” of Aquila, the Eagle, is the southernmost a part of the triangle; one can think about it because the tip of a triangle pointing south. From Altair, one can look straight up and see Deneb on the left and Vega on the fitting to finish the Triangle. Deneb is the tail of Cygnus, the Swan.
Vega is the brightest star in Lyra, the Lyre. The constellation Cygnus varieties a cross form and it’s generally known as the Northern Cross; if one follows the lengthy axis of the cross roughly in direction of Altair, one reaches the star Sadr, the middle of the cross, after which Albireo, the “head” of the Swan.
Drawing a line between Deneb and Altair takes you to Sagittarius; near the horizon within the south. Sagittarius has a definite “teapot” form of seven stars. Scorpius (the Scorpion) will probably be practically setting, although the center of the Scorpion, Antares, continues to be simply excessive sufficient to see if the horizon is obvious of obstructions; it is just about 9 levels excessive from the latitude of New York.
Above Scorpius one can see Ophiuchus; the Serpent Bearer. To seek out it, search for Antares, after which upwards from the horizon; one ought to see a big rectangle of fainter stars with a brief horizontal facet and longer vertical ones; that’s the physique of Ophiuchus, and above the rectangle is a star that makes an “A-frame” form, which is his head. Ophiuchus is typically known as a 13th constellation of the zodiac, as a result of the constellation’s fashionable borders imply the solar and planets typically move by means of it.
Constellations seen within the Southern Hemisphere on Sept. 21 at about 9 p.m. native time will embody the Southern Cross, Centaurus the Centaur, and the Southern Fish. From mid-southern latitudes corresponding to Cape City or Santiago, Chile, or Melbourne, Australia, The Southern Cross (formally known as Crux) is within the southwest, about 21 levels above the horizon. It is a compact group and the underside of the cross, marked by Acrux, faces roughly in direction of the Southern Celestial Pole (on this case the underside of the cross is to the left, as a result of the Cross will seem sideways). Above the Cross are two vibrant stars; the primary one (as one strikes upwards) is Hadar, and the second is Rigil Kentaurus, in any other case referred to as Alpha Centauri. These are generally taken to be the entrance hooves or legs of the Centaur.
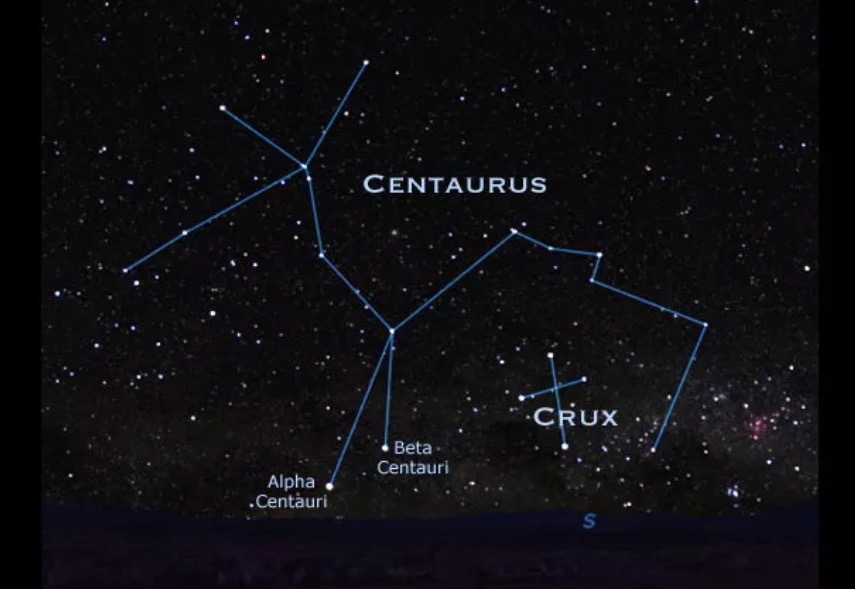
Turning in direction of the southeast (to the left) one will see a vibrant star that at 9 p.m. native time will probably be at about the identical altitude because the Cross (think about drawing a straight horizontal line virtually midway throughout the sky). That is Achernar, the tip of Eridanus, the River. The River extends under the horizon (the remainder of it does not rise till later) however the different finish is close to the foot of Orion.
If one continues turning left (in direction of the east) and upwards, about midway to the zenith, one encounters Fomalhaut, the brightest star in Piscis Austrinus, the Southern Fish. Fomalhaut is west and south of Saturn, placing it above and to the fitting of the ringed planet. From the Northern Hemisphere it’s at all times near the horizon and troublesome to see however within the Southern Hemisphere it will get a lot increased within the sky.
Turning to the north (left from Fomalhaut and Saturn), one can see the Summer season Triangle, however from under the equator it’s “the other way up” with Vega nearer to the horizon, about 16 levels excessive (this can change a bit relying on one’s actual latitude), with Altair above and to the fitting. Deneb is difficult to see from the southern latitudes; it will likely be to the fitting of Vega however solely about 9 to 10 levels above the horizon.
Within the excessive western sky — above Mars — one can spot an upside-down Scorpius, which within the southern skies faces in direction of the horizon and is way increased, with Antares about 53 levels excessive if one is on the latitude of Santiago, Chile or Sydney, Australia. Sagittarius can be excessive within the sky; virtually straight overhead.

