[ad_1]
An enormous blob of abnormally sizzling rock beneath the Appalachian Mountains fashioned when Greenland separated from North America round 80 million years in the past, new analysis suggests.
Scientists beforehand thought that this sizzling zone, often called the Northern Appalachian Anomaly, was left over after North America broke away from Africa 180 million years in the past, however this idea doesn’t stand as much as new scrutiny, in response to the research, revealed Wednesday (July 30) within the journal Geology.
“This thermal upwelling has lengthy been a puzzling characteristic of North American geology,” lead writer Thomas Gernon, a professor of Earth science on the College of Southampton within the U.Okay., mentioned in a assertion. “It lies beneath a part of the continent that is been tectonically quiet for 180 million years, so the concept that it was only a leftover from when the landmass broke aside by no means fairly stacked up.”
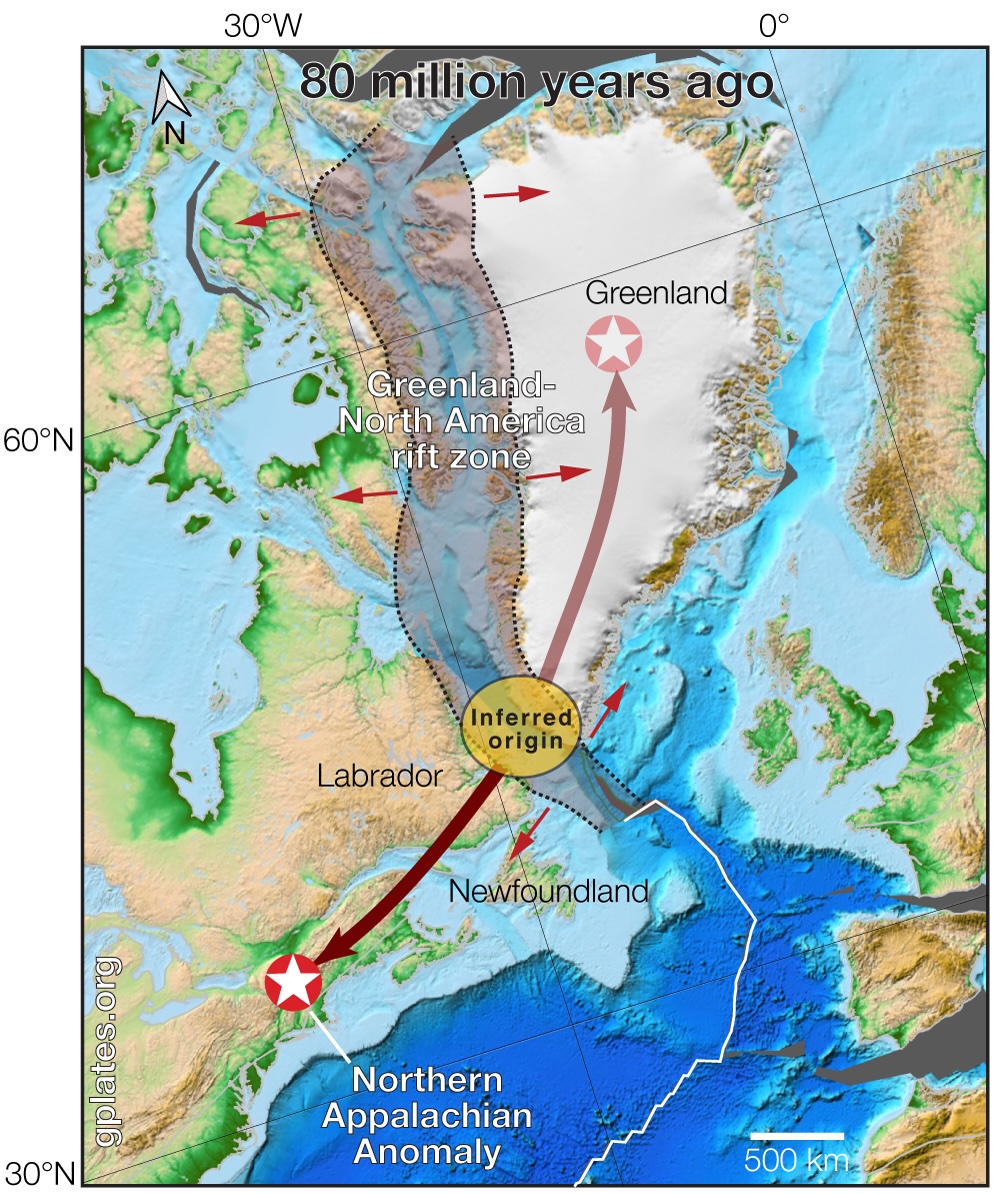
As an alternative, the brand new findings point out that the recent blob, which sits 125 miles (200 kilometers) deep and stretches 220 miles (350 km) throughout New England, appeared round 80 million years in the past, when what are actually Greenland and Canada have been breaking up. The outcomes recommend that such blobs often type in continent breakups, with attainable knock-on results for mountains, volcanoes and ice sheets.
Gernon and colleagues described how sizzling blobs type in a research revealed final yr within the journal Nature. Scorching blobs are created when materials from Earth’s mantle rises to fill gaps within the crust left by rifting. This materials finally cools and turns into so dense that it sinks, or “drips,” setting off chain reactions within the mantle that the researchers referred to as “mantle waves.”
There could also be particular circumstances required for mantle waves to type, Gernon informed Stay Science in an e mail, together with a steep temperature gradient the place the dripping materials enters the mantle. Which means not all continent breakups create mantle waves, Gernon mentioned.
Associated: North America is ‘dripping’ down into Earth’s mantle, scientists uncover
For the brand new research, the researchers used direct geological observations and pc simulations to mannequin plate tectonics and geodynamics. They simulated the initiation of a sizzling blob 1,120 miles (1,800 km) northeast of the Appalachians and located that geologic processes pushed the blob southwest at a fee of 12 miles (20 km) each million years. These outcomes have been per earlier estimates, in response to the assertion.
The group’s simulations confirmed that the recent blob could have helped to uplift the Appalachian Mountains when it obtained there, fixing the long-standing query of why the Appalachians stay so excessive regardless of main erosion over the previous 20 million years.
“Warmth on the base of a continent can weaken and take away a part of its dense root, making the continent lighter and extra buoyant, like a sizzling air balloon rising after dropping its ballast,” Gernon defined within the assertion. “This is able to have precipitated the traditional mountains to be additional uplifted over the previous million years.”
Scorching blobs elsewhere might clarify why mountains with a geology just like the Appalachians are nonetheless standing, Gernon mentioned. These blobs might additionally clarify uncommon volcanic eruptions that carry diamonds to Earth’s floor, in response to the assertion.
Greenland’s blob
The research centered totally on the Northern Appalachian Anomaly, however the researchers additionally examined its “twin” — a sizzling blob at present sitting beneath north-central Greenland. That anomaly was born in the identical continental breakup occasion, however on the opposite aspect of the rift, in response to the assertion. The group famous that it creates warmth currents beneath the Greenland Ice Sheet that affect how the ice strikes and melts right this moment.
“Historical warmth anomalies proceed to play a key function in shaping the dynamics of continental ice sheets from under,” Gernon mentioned. “Regardless that the floor exhibits little signal of ongoing tectonics, deep under, the implications of historical rifting are nonetheless taking part in out.”
The Northern Appalachian Anomaly continues to be on the transfer, and the researchers estimate that it’s going to proceed on its path to achieve New York in 10 million to fifteen million years.
As soon as the recent blob leaves the Appalachians, Earth’s crust there’ll settle once more, Gernon mentioned. “Within the absence of additional tectonic or mantle-driven uplift, erosion would proceed to put on down the mountains, regularly reducing their elevation,” he mentioned.
Total, the outcomes reveal that continent breakups and different main geological occasions can proceed to affect the planet for 1000’s, and even thousands and thousands, of years, the researchers mentioned within the assertion.
“The concept rifting of continents may cause drips and cells of circulating sizzling rock at depth that unfold 1000’s of kilometers inland makes us rethink what we all know in regards to the edges of continents each right this moment and in Earth’s deep previous,” research co-author Derek Keir, an affiliate professor of Earth science on the College of Southampton and the College of Florence in Italy, mentioned within the assertion.
[ad_2]

