[ad_1]

Smoking helps oral micro organism settle within the intestine, defending towards colitis however not Crohn’s illness. This mechanism may encourage safer therapies.
A analysis crew led by Hiroshi Ohno on the RIKEN Heart for Integrative Medical Sciences (IMS) in Japan has uncovered why smoking tobacco seems to ease signs in individuals with ulcerative colitis, a power situation marked by irritation within the giant gut.
Their examine, printed within the journal Intestine, revealed that smoking produces sure metabolites that enable oral micro organism to determine themselves within the colon, the place they activate an immune response. The findings recommend that related advantages is likely to be achieved by means of options equivalent to prebiotics like hydroquinone or probiotic therapies utilizing micro organism equivalent to Streptococcus mitis, eradicating the necessity for smoking and its well-known well being dangers.
Inflammatory bowel illness exists in two principal types: Crohn’s illness and ulcerative colitis. Each trigger recurring belly ache, diarrhea, fatigue, and weight reduction, however they differ of their underlying causes, the precise areas of the intestine they have an effect on, and the sorts of irritation they produce.
For greater than 4 a long time, researchers have been puzzled by the paradox that smoking raises the chance of Crohn’s illness whereas on the similar time providing some safety towards ulcerative colitis. As a result of each situations contain immune-driven irritation within the intestine, and since intestine immunity is strongly formed by the microbial neighborhood dwelling there, Ohno and his colleagues got down to take a look at whether or not the contrasting results of smoking may very well be traced again to variations in intestine micro organism.
Smoking adjustments intestine micro organism
The crew mixed human medical information with mouse experiments to analyze the phenomenon. In sufferers with ulcerative colitis, they noticed that people who smoke had micro organism sometimes discovered within the mouth, equivalent to Streptococcus, colonizing the intestine—particularly within the colonic mucosa that strains the gut. This was not the case for former people who smoke. Below regular situations, oral micro organism swallowed with saliva move by means of the digestive tract with out establishing themselves, however smoking appeared to allow these microbes to take root within the intestine mucosa.
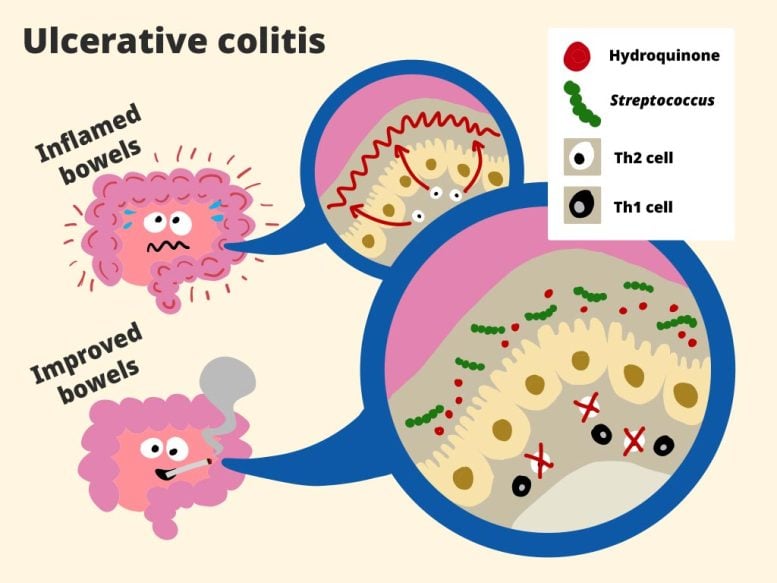
The subsequent step was to find out why. The researchers analyzed intestine metabolites—small molecules generated throughout digestion and microbial exercise. They discovered that people who smoke with ulcerative colitis had larger ranges of a number of metabolites in comparison with ex-smokers with the illness. In mouse fashions, certainly one of these metabolites, hydroquinone, was proven to stimulate the expansion of Streptococcus within the intestine lining. This prompt that smoking-related metabolites, equivalent to hydroquinone, create situations that enable oral micro organism to thrive within the intestinal mucus layer. However questions remained: how do these microbes cut back irritation in colitis, and why do they not produce the identical impact in Crohn’s illness?
To discover additional, the crew remoted 10 bacterial strains from the saliva of people who smoke whose oral microbes had colonized the intestine mucosa. These strains have been then administered to mouse fashions of each Crohn’s illness and ulcerative colitis for 5 days. The outcomes revealed that remedy with Streptococcus mitis produced results practically similar to these seen with smoking: irritation decreased in mice with ulcerative colitis however worsened in these with Crohn’s illness.
How S. mitis impacts immunity
Evaluation confirmed that S. mitis triggered the emergence of helper Th1 cells, that are an essential a part of the intestine’s immune response to invaders. In Crohn’s illness this possible worsens the situation as a result of the unique irritation is definitely brought on by these similar helper Th1 cells. However in colitis, the Th1 cells battle towards an preliminary Th2-immune response, and this finally ends up lowering irritation.
As smoking poses excessive dangers for most cancers, coronary heart illness, and plenty of different sicknesses, it isn’t a sustainable remedy for ulcerative colitis. “Our outcomes point out the relocation of micro organism from the mouth to the intestine, significantly these of the Streptococcus genus, and the next immune response within the intestine, is the mechanism by means of which smoking helps defend towards the illness,” says Ohno. “Logically, direct remedy with this sort of micro organism, or oblique remedy with hydroquinone, is thus prone to mimic the helpful results of smoking however keep away from all of the adverse results.”
Reference: “Smoking impacts intestine immune system of sufferers with inflammatory bowel ailments by modulating metabolomic profiles and mucosal microbiota” by Eiji Miyauchi, Takashi Taida, Kan Uchiyama, Yumiko Nakanishi, Tamotsu Kato, Shigeo Koido, Nobuo Sasaki, Toshifumi Ohkusa, Nobuhiro Sato and Hiroshi Ohno, 25 August 2025, Intestine.
DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2025-334922
By no means miss a breakthrough: Be part of the SciTechDaily publication.
[ad_2]

