[ad_1]
When you consider ticks, you may image nightmarish little parasites, stalking you on weekend hikes or afternoons within the park.
Your concern is well-founded. Tick-borne illnesses are the most prevalent vector-borne illnesses — these transmitted by residing organisms — in the US. Every tick feeds on a number of animals all through its life, absorbing viruses and micro organism alongside the way in which and passing them on with its subsequent chew. A few of these viruses and micro organism are dangerous to people, inflicting illnesses that may be debilitating and typically deadly with out therapy, similar to Lyme, babesiosis and Rocky Mountain noticed fever.
However contained in each chew of this infuriating, insatiable pest can also be a trove of social, environmental and epidemiological historical past.
In lots of instances, human actions way back are the explanation ticks carry these illnesses so extensively as we speak. And that’s what makes ticks fascinating for environmental historians like me.
Altering forests fueled tick dangers
Through the 18th and nineteenth centuries, settlers cleared greater than half the forested land throughout the northeastern U.S., reducing down forests for timber and to make manner for farms, cities and mining operations. With large-scale land clearing got here a pointy decline in wildlife of all types. Predators similar to bears and wolves had been pushed out, as had been deer.
As farming moved westward, Northeasterners started to acknowledge the ecological and financial worth of timber, and so they returned tens of millions of acres to forest.
The woods regrew. Plant-eaters similar to deer returned, however the apex predators that when stored their populations in test didn’t.
Because of this, deer populations grew quickly. With the deer got here deer ticks (Ixodes scapularis) carrying Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme illness. When a tick feeds on an contaminated animal, it may well take up the micro organism. The tick can go the micro organism to its subsequent sufferer. In people, Lyme illness may cause fever and fatigue, and if left untreated it may well have an effect on the nervous system.
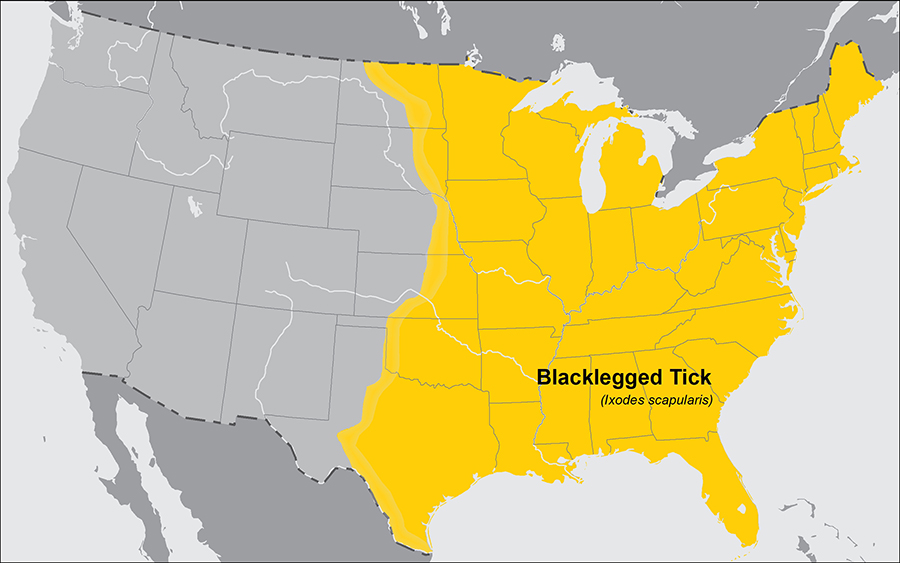
The japanese U.S. turned a worldwide sizzling spot for tick-borne Lyme illness beginning across the Seventies. Lyme illness affected over 89,000 Individuals in 2023, and presumably many extra.
Californians transfer into tick territory
For hundreds of years, altering patterns of human settlements and the politics of land use have formed the function of ticks and tick-borne sicknesses inside their environments.
Briefly, people have made it simpler for ticks to thrive and unfold illness in our midst.
In California, the Northern Internal Coast and Santa Cruz mountain ranges that converge on San Francisco from the north and south had been by no means clear-cut, and predators similar to mountain lions and coyotes nonetheless exist there. However competitors for housing has pushed human settlement deeper into wildland areas to the north, south and east of the town, reshaping tick ecology there.
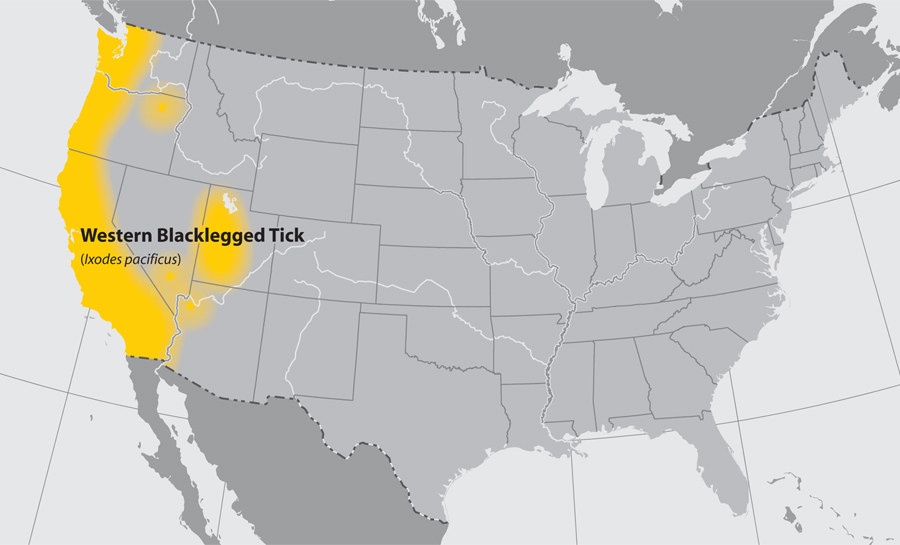
Whereas western black-legged ticks (Ixodes pacificus) are likely to swarm in massive forest preserves, the Lyme-causing bacterium is definitely extra prevalent in small, remoted patches of greenery. In these remoted patches, rodents and different tick hosts can thrive, protected from massive predators, which want extra habitat to maneuver freely. However isolation and decrease range additionally means infections are unfold extra simply inside the tick’s host populations.
Folks have a tendency to construct remoted homes within the hills, slightly than massive, related developments. Because the Silicon Valley space south of San Francisco sprawls outward, this checkerboard sample of settlement has fragmented the pure panorama, making a hard-to-manage public well being menace.
Fewer hosts, extra tightly packed, typically means extra contaminated hosts, proportionally, and thus extra harmful ticks.
Six counties throughout these ranges, all surrounding and together with San Francisco, account for 44% of recorded tick-borne sicknesses in California.
A lesson from Texas cattle ranches
Domesticated livestock have additionally formed the illness menace posed by ticks.
In 1892, at a gathering of cattle ranchers on the Inventory Raiser’s Conference in Austin, Texas, Dr. B.A. Rogers launched a novel idea that ticks had been behind latest devastating plagues of Texas cattle fever. The illness had arrived with cattle imported from the West Indies and Mexico within the 1600s, and it was taking large tolls on cattle herds. However how the illness unfold to new victims had been a thriller.
Editors of Daniel’s Texas Medical Journal discovered the concept of ticks spreading illness laughable and lampooned the speculation, publishing a satire of what they described as an “early copy” of a forthcoming report on the topic.
The tick’s “fluid secretion, it’s believed, is the poison which causes the fever … [and the tick] having been identified to chew tobacco, as all different Texans do, the secretion is most likely tobacco juice,” they wrote.
Fortuitously for the ranchers, to not point out the cows, the U.S. Division of Agriculture sided with Rogers. Its cattle fever tick program, began in 1906, curbed cattle fever outbreaks by limiting the place and when cattle ought to cross tick-dense areas.
By 1938, the federal government had established a quarantine zone that prolonged 580 miles by 10 miles alongside the U.S.-Mexico border in South Texas Brush Nation, a area favored by the cattle tick.
This progressive use of pure house as a public well being device helped to functionally eradicate cattle fever from 14 Southern states by 1943.
Ticks are merchandise of their atmosphere
On the subject of tick-borne illnesses the world over, location issues.
Take the hunter tick (Hyalomma spp.) of the Mediterranean and Asia. As a juvenile, or nymph, these ticks feed on small forest animals similar to mice, hares and voles, however as an grownup they like domesticated livestock.
For hundreds of years, this tick was an occasional nuisance to nomadic shepherds of the Center East. However within the 1850s, the Ottoman Empire handed legal guidelines to pressure nomadic tribes to turn into settled farmers as a substitute. Unclaimed lands, particularly on the forested edges of the steppe, had been supplied to settlers, creating preferrred situations for hunter ticks.
Because of this, farmers in what as we speak is Turkey noticed spikes in tick-borne illnesses, together with a virus that causes Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, a probably deadly situation.
It’s in all probability an excessive amount of to ask for sympathy for any ticks you meet this summer time. They’re bloodsucking parasites, in spite of everything.
Nonetheless, it’s price remembering that the tick’s malevolence isn’t its personal fault. Ticks are merchandise of their atmosphere, and people have performed many roles in turning them into the dangerous parasites that search us out as we speak.
This edited article is republished from The Dialog below a Artistic Commons license. Learn the authentic article.
[ad_2]

