[ad_1]
Scientists are one step nearer to understanding how human ovaries develop their lifetime provide of egg cells, referred to as ovarian reserve.
The brand new analysis, revealed Aug. 26 within the journal Nature Communications, mapped the emergence and development of the cells and molecules that grow to be the ovarian reserve in monkeys, from the early levels of ovarian growth in an embryo to 6 months after beginning.
This map fills in a number of the blanks in “actually vital areas of simply unknown biology,” examine co-author Amander Clark, a developmental biologist at UCLA, instructed Dwell Science.
Researchers can now use this map to construct higher fashions of the ovary within the lab to check reproductive illnesses associated to the ovarian reserve, she stated, corresponding to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) — a fancy hormonal dysfunction that can lead to infertility.
Mysterious growth
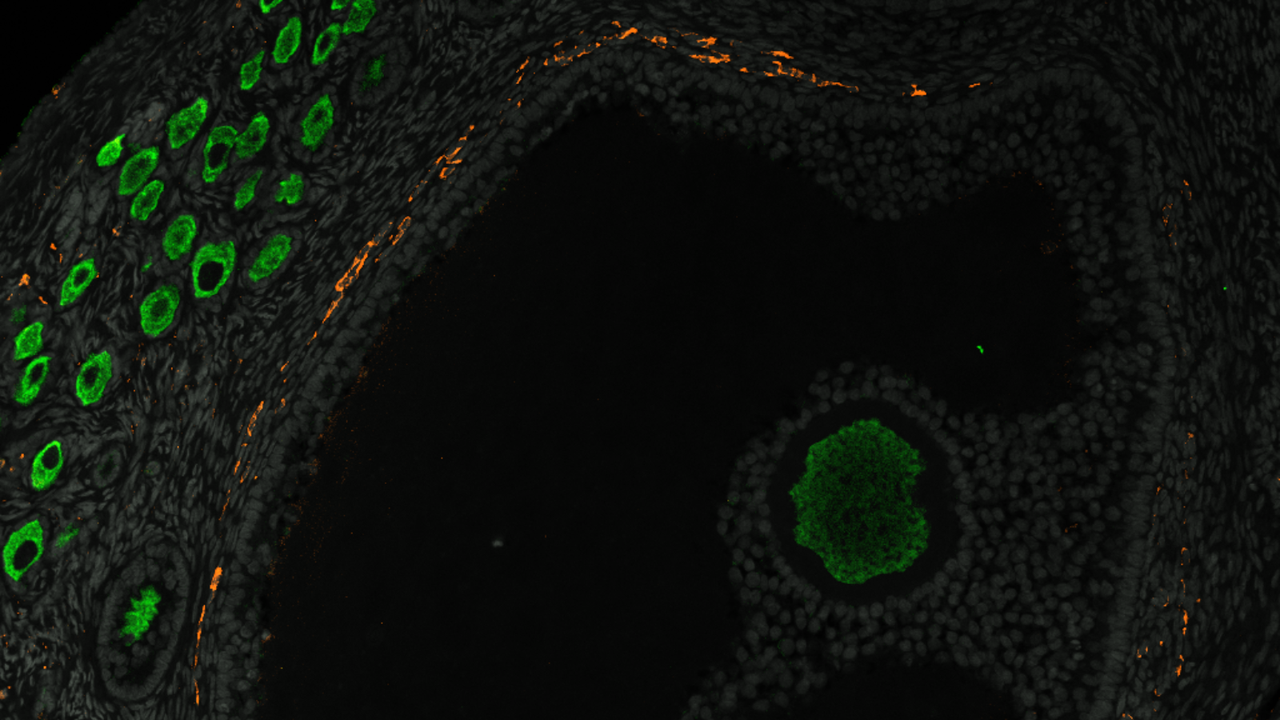
Ovaries first start to develop in embryos round six weeks after fertilization. Within the early levels, germ cells — which grow to be egg cells — divide and join to 1 one other in advanced chains referred to as nests. When these nests burst open, particular person egg cells are launched and are encased by a layer of specialised cells referred to as pregranulosa cells, which help the younger eggs and sign when it is time to mature.
These eggs encircled by pregranulosa cells are referred to as primordial follicles, and are what make up the ovarian reserve.
Primordial follicles begin to kind round 20 weeks after fertilization, and cluster on the within edges of the ovaries. When the follicles closest to the middle of the ovary in these clusters mature, they develop and produce intercourse hormones.
So it’s the primordial follicles that make sure the ovaries carry out their jobs of manufacturing mature eggs and releasing hormones, Clark stated.
A number of ovarian illnesses and circumstances are rooted in issues with the cells within the ovarian reserve. For instance, though the precise reason for PCOS remains to be unknown, it includes dysfunction within the primordial follicles. And but, little or no work has been completed to grasp their growth.
Constructing a map of how and when the ovarian reserve types throughout being pregnant can assist determine why sure illnesses and points with fertility crop up later in life. “That is the place this examine got here in,” Clark stated.
Associated: 1st ‘atlas’ of human ovaries might result in fertility breakthrough, scientists say
Shock findings
To research how ovarian reserves originate in primates, Clark and her group checked out a monkey species that’s physiologically just like people. This makes it a very good stand-in for what occurs developmentally in people, she stated.
Then, the group analyzed the place and molecular fingerprint of the ovarian cells to grasp the crucial occasions within the formation of the ovarian reserve.
They discovered that pregranulosa cells fashioned in two waves, but it surely was solely through the second wave, between days 41 and 52, that pregranulosa cells fashioned that will go on to swarm the younger eggs to kind primordial follicles.
In addition they recognized two genes that appear to be energetic previous to this second wave. The researchers stated that trying additional into the operate of those genes might assist to pinpoint the developmental origins of ovarian reserve issues.
Additionally, Clark stated the group was utterly stunned to seek out that “earlier than beginning, the ovary goes by observe rounds of folliculogenesis,” which means that very quickly after the ovarian reserve is made, a number of the extra centrally positioned follicles mature and may produce hormones. The researchers counsel that figuring out why these follicles usually activate might present perception into the causes of PCOS.
Nonetheless, the researchers are a extremely dynamic interval in growth, when the mobile make-up of an embryo can change dramatically, Luz Garcia-Alonso, a computational biologist on the Wellcome Sanger Institute who was not concerned within the examine, instructed Dwell Science in an electronic mail. And so they have massive time gaps between their remark durations.
“This stage when cell lineages are specified could be very dynamic, and cell composition adjustments inside days,” Garcia-Alonso stated. So the group ought to accumulate extra fine-scale knowledge on extra time factors to get a greater image of what’s going on, she added.
This text is for informational functions solely and isn’t meant to supply medical recommendation.
[ad_2]

