[ad_1]
One summer season evening in 1877, American astronomer Asaph Corridor was trying by way of his telescope in Washington, D.C. Mars was at its closest level to Earth in its orbit, and Corridor had one query on his thoughts: Does the Crimson Planet have a moon?
After a number of nights of looking in heavy fog, Corridor noticed not only one however two moons, which he named Phobos and Deimos, the “terror” and “panic” twins in Greek mythology whose dad and mom have been Ares and Aphrodite (Mars and Venus in Roman mythology). These moons, nonetheless, look very totally different from our personal — and scientists nonetheless have a variety of questions on their origins.
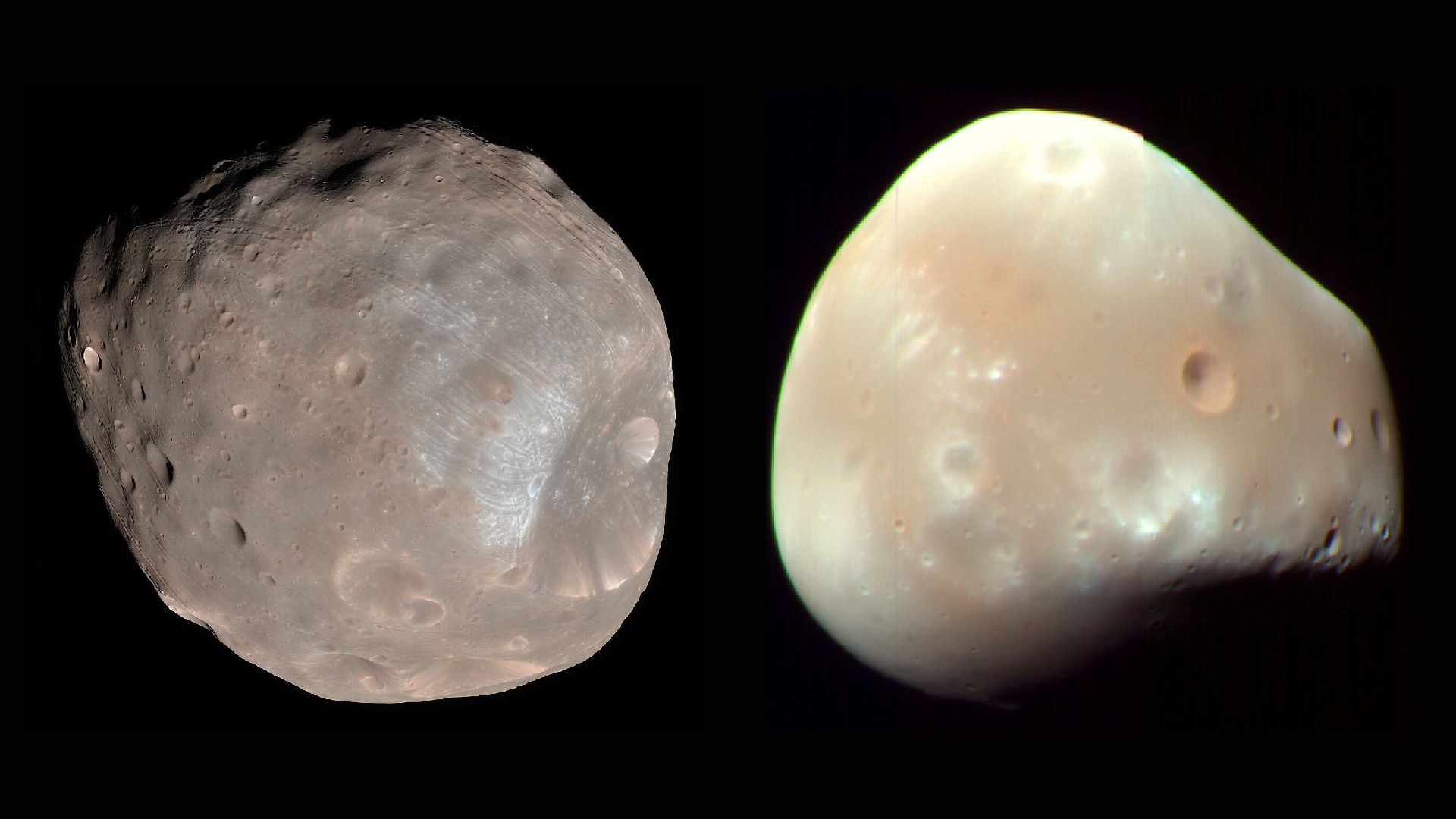
“Phobos and Deimos are among the smallest moons in our photo voltaic system,” Christopher S. Edwards, a professor of astronomy and planetary science at Northern Arizona College, advised Dwell Science in an e mail.
In contrast with our moon, which measures 2,159 miles (3,475 kilometers) throughout, Phobos and Deimos are simply tiny specks within the sky. On common, Phobos measures simply 14 miles (22 km) throughout, and Deimos is even smaller, about 7 miles (12 km) throughout on common. Their width shouldn’t be constant as a result of these two tiny moons aren’t completely spherical.
“They’re type of bumpy, potato formed, and are actually, actually darkish, just like the brightness of latest asphalt,” Edwards defined.
A moon is outlined as any naturally-formed physique that completely orbits a planet. However due to their irregular form and miniature measurement, many scientists say that Phobos and Deimos look extra like asteroids than moons.
It is doable that Mars’ moons have been initially asteroids that have been captured by the planet’s gravitational pull. There’s additionally a principle that the 2 moons have been created after a big object collided with Mars, creating particles that fashioned the 2 lunar our bodies, much like how Earth’s moon probably fashioned. Each of those hypotheses are nonetheless up for debate.
Associated: What number of moons are within the photo voltaic system?
“How the moons of Mars fashioned is a serious open query for science,” Nancy Chabot, chief scientist for the House Exploration Sector on the Johns Hopkins Utilized Physics Laboratory, advised Dwell Science in an e mail.
For now, there’s proof on either side. Seen and shortwave infrared spectral analyses of the moons level towards a composition in line with asteroids, however it’s additionally troublesome to clarify the physics behind Mars snatching up two asteroids, Edwards mentioned. That is as a result of Mars has a comparatively weak gravitational pull, and the form and placement of the 2 moons’ orbits can be difficult to realize by way of asteroid seize. Edwards added that knowledge from the Hope Emirates Mars Mission suggests the 2 moons have barely totally different compositions, additional complicating issues.
However an upcoming mission to Mars could quickly present extra solutions. The Martian Moons Exploration (MMX) mission by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA), deliberate to launch in 2026, will journey to Mars and discover its two moons, and even convey a pattern from Phobos again to Earth.
“JAXA’s MMX mission could be very thrilling and is ready to be the primary to unravel the mysteries of the Martian moons, together with answering how they fashioned,” Chabot mentioned.
Analyzing the composition of this pattern will assist make clear Phobos’ and Deimos’ origin, as a result of a moon that was as soon as an asteroid would have a really totally different chemical composition to a moon that fashioned from chunks of early Mars.
If the Phobos pattern signifies that the moons fashioned from a collision with Mars, it may open the door to much more thrilling discoveries. In that case, the pattern may make clear whether or not the early Crimson Planet had the potential for extraterrestrial life.
“These may in truth be samples of early Mars,” which can have as soon as been hospitable for all times, Edwards mentioned.
Mars quiz: Is your data of the Crimson Planet out of this world?
[ad_2]

