After Christmas dinner in 2021, our household was glued to the tv, watching the nail-biting launch of NASA’s $10 billion James Webb House Telescope. There had not been such a leap ahead in telescope expertise since Hubble was launched in 1990.
En path to its deployment, Webb needed to efficiently navigate 344 potential factors of failure. Fortunately, the launch went higher than anticipated, and we might lastly breathe once more.
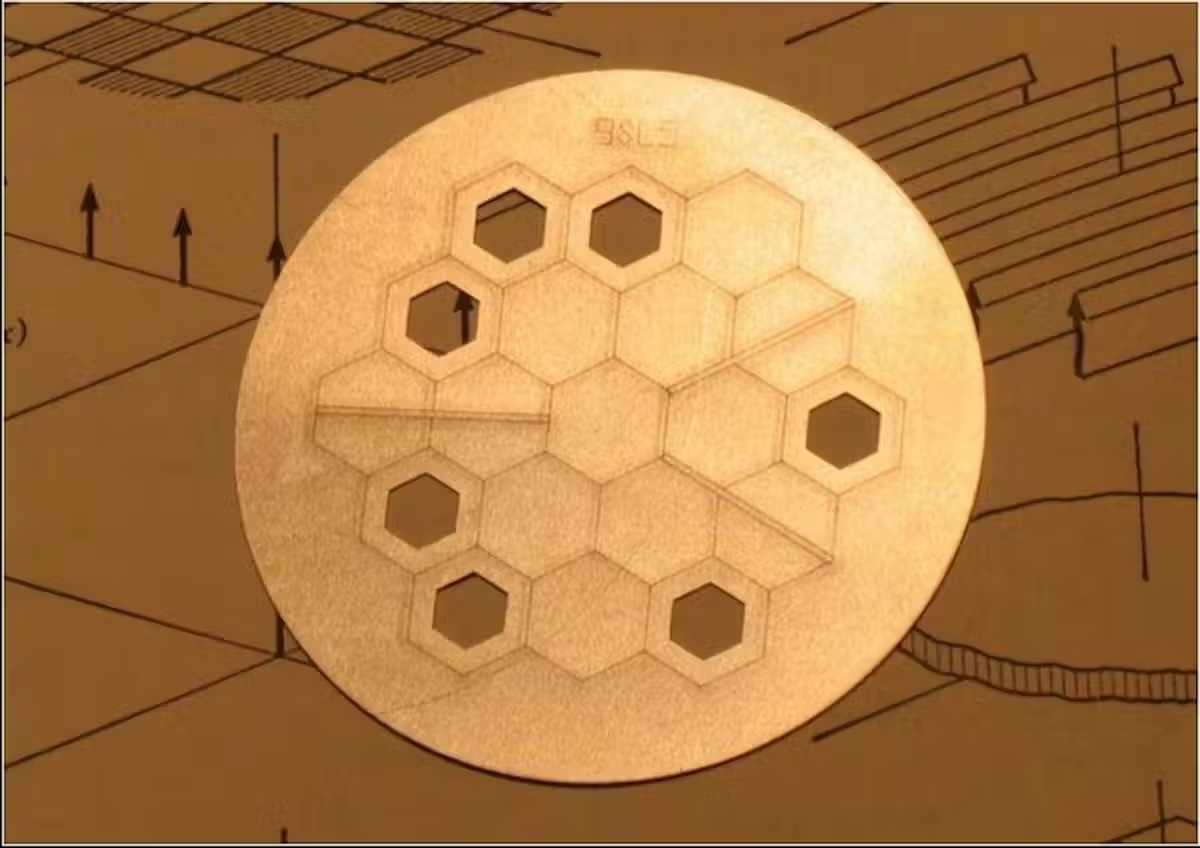
We might be utilizing Webb’s highest-resolution mode, known as the aperture masking interferometer or AMI for brief. It is a tiny piece of exactly machined metallic that slots into one of many telescope’s cameras, enhancing its decision.
Our outcomes on painstakingly testing and enhancing AMI at the moment are launched on the open-access archive arXiv in a pair of papers. We will lastly current its first profitable observations of stars, planets, moons and even black gap jets.
Working with an instrument 1,000,000 miles away
Hubble began its life seeing out of focus — its mirror had been floor exactly, however incorrectly. By taking a look at identified stars and evaluating the perfect and measured photos (precisely like what optometrists do), it was potential to determine a “prescription” for this optical error and design a lens to compensate.
The correction required seven astronauts to fly up on the House Shuttle Endeavor in 1993 to put in the brand new optics. Hubble orbits Earth just some hundred miles above the floor, and will be reached by astronauts.
In contrast, Webb is roughly 1 million miles (1.5 million km) away — we won’t go to and repair it, and want to have the ability to repair points with out altering any {hardware}.
That is the place AMI is available in. That is the one Australian {hardware} on board, designed by astronomer Peter Tuthill.
It was placed on Webb to diagnose and measure any blur in its photos. Even nanometers of distortion in Webb’s 18 hexagonal major mirrors and lots of inner surfaces will blur the photographs sufficient to hinder the examine of planets or black holes, the place sensitivity and determination are key.
AMI filters the sunshine with a fastidiously structured sample of holes in a easy metallic plate, to make it a lot simpler to inform if there are any optical misalignments.
Searching blurry pixels
We wished to make use of this mode to look at the beginning locations of planets, in addition to materials being sucked into black holes. However earlier than any of this, AMI confirmed Webb wasn’t working solely as hoped.
At very fantastic decision — on the stage of particular person pixels — all the photographs have been barely blurry on account of an digital impact: brighter pixels leaking into their darker neighbors.
This isn’t a mistake or flaw, however a basic characteristic of infrared cameras that turned out to be unexpectedly critical for Webb.
This was a dealbreaker for seeing distant planets many hundreds of instances fainter than their stars a couple of pixels away: my colleagues rapidly confirmed that its limits have been greater than ten instances worse than hoped.
So, we got down to appropriate it.
How we sharpened Webb’s imaginative and prescient
In a brand new paper led by College of Sydney PhD pupil Louis Desdoigts, we checked out stars with AMI to be taught and proper the optical and digital distortions concurrently.
We constructed a pc mannequin to simulate AMI’s optical physics, with flexibility in regards to the shapes of the mirrors and apertures and in regards to the colors of the celebs.
We related this to a machine studying mannequin to characterize the electronics with an “efficient detector mannequin” — the place we solely care about how properly it may possibly reproduce the info, not about why.
After coaching and validation on some take a look at stars, this setup allowed us to calculate and undo the blur in different knowledge, restoring AMI to full perform. It does not change what Webb does in area, however moderately corrects the info throughout processing.
It labored fantastically — the star HD 206893 hosts a faint planet and the reddest-known brown dwarf (an object between a star and a planet). They have been identified however out of attain with Webb earlier than making use of this correction. Now, each little dots popped out clearly in our new maps of the system.
This correction has opened the door to utilizing AMI to prospect for unknown planets at beforehand unimaginable resolutions and sensitivities.
It really works not simply on dots
In a companion paper by College of Sydney PhD pupil Max Charles, we utilized this to trying not simply at dots — even when these dots are planets — however forming advanced photos on the highest decision made with Webb. We revisited well-studied targets that push the boundaries of the telescope, testing its efficiency.
With the brand new correction, we introduced Jupiter’s moon Io into focus, clearly monitoring its volcanoes because it rotates over an hour-long timelapse.
As seen by AMI, the jet launched from the black gap on the centre of the galaxy NGC 1068 intently matched photos from much-larger telescopes.
Lastly, AMI can sharply resolve a ribbon of mud round a pair of stars known as WR 137, a faint cousin of the spectacular Apep system, lining up with idea.
The code constructed for AMI is a demo for far more advanced cameras on Webb and its follow-up, Roman area telescope. These instruments demand an optical calibration so fantastic, it is only a fraction of a nanometre — past the capability of any identified supplies.
Our work reveals that if we are able to measure, management, and proper the supplies we do should work with, we are able to nonetheless hope to search out Earth-like planets within the far reaches of our galaxy.
This edited article is republished from The Dialog beneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the authentic article.

