Mars might have had its personal model of an Ice Age that reshaped elements of the Purple Planet and carved deep “scratches” in its floor that stay seen right now.
New high-resolution photos from the European House Company’s (ESA) Mars Specific orbiter present ridges, troughs and swirl-like textures that bear a outstanding resemblance to glacial formations on Earth. Noticed in a rugged mid-latitude area known as Coloe Fossae, these options probably shaped as ice combined with rock and mud crept via valleys and pooled inside affect craters, suggesting glaciers as soon as flowed removed from the planet’s poles, reshaping valleys and craters of their path, in response to a press release from ESA.
Ice ages are pure local weather cycles pushed by refined shifts in a planet’s orbit and tilt, which change how daylight falls throughout its floor. As temperatures swing over time, glaciers develop and retreat, reshaping the panorama. On Mars, these historic rhythms left behind the frozen scars now seen in areas like Coloe Fossae, which lies round 39 levels north of the equator — properly outdoors the polar areas the place Martian ice is normally discovered.
Coloe Fossae was formed by highly effective tectonics, which stretched and cracked Mars’s crust, inflicting chunks of floor to break down and type lengthy, parallel troughs. Traces of particles may be seen within the swirling deposits discovered on the backside of deep valleys and affect craters scattered throughout the area.
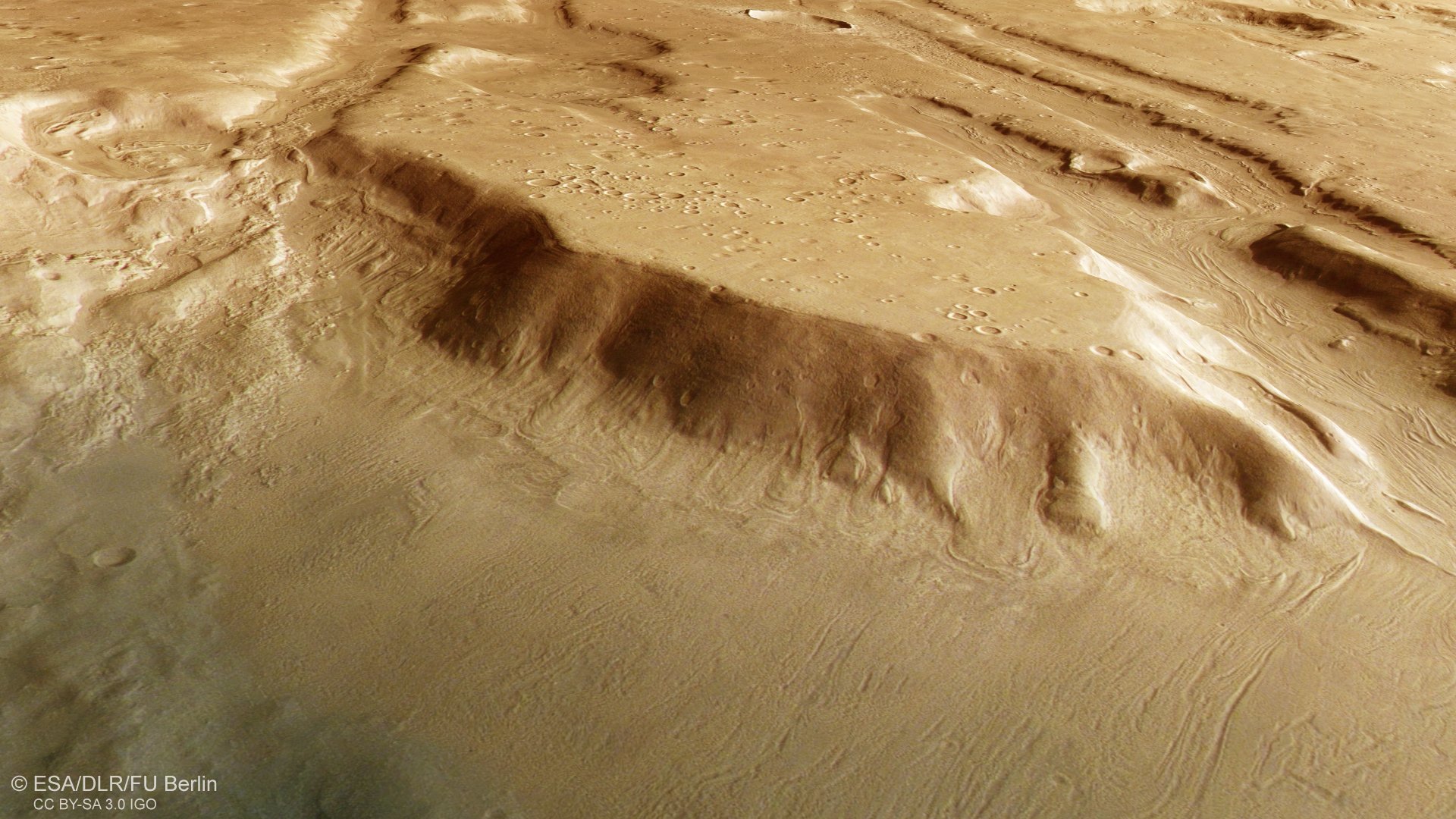
Researchers imagine that these deposits appeared throughout a previous Martian ice age, when the planet’s tilt shifted dramatically. When Mars leans extra steeply on its axis, daylight patterns change, inflicting polar ice emigrate towards the mid-latitudes. As the lean lessens, the ice retreats once more, carving and refilling terrain in rhythmic cycles that mirror Earth’s personal glacial epochs.
“Though Mars is at the moment dry, it has skilled alternating durations of heat and chilly, freeze and thaw, all through its historical past, pushed by modifications within the tilt of its axis,” researchers mentioned within the assertion.
The swirling deposits and flow-like textures in Coloe Fossae present clear proof of Mars’s dynamic local weather historical past, exhibiting how ice as soon as formed mid-latitude landscapes. These findings give scientists useful insights into the timing and patterns of previous ice ages on Mars, serving to to refine fashions of the planet’s geological and climatic evolution over tens of millions of years.

